Table of Contents
ToggleWhy Smoking After a Hair Transplant Is Discouraged
Smoking after a hair transplant is strongly discouraged due to nicotine’s detrimental impact on the healing process. Nicotine constricts blood vessels, reducing oxygen and nutrient delivery to the transplanted follicles, which is crucial for their survival and growth.
The Importance of Avoiding Nicotine
During the recovery phase, it’s vital to keep the transplanted hair follicles healthy and well-nourished. Exposure to nicotine can compromise the success of the transplant, leading to complications and suboptimal results.
Recommended Waiting Period
- Minimum Waiting Period: Avoid smoking for at least 7 days post-surgery.
- Ideal Waiting Period: Wait 3-4 months before resuming smoking to ensure optimal healing and transplant success.
- Total Cessation: Consider quitting smoking altogether for better overall health and transplant outcomes.
Risks of Smoking Post-Hair Transplant
- Extended Recovery Time: Smoking hampers blood flow, slowing down the healing process.
- Increased Infection Risk: Reduced oxygen supply increases susceptibility to infections.
- Impaired Hair Growth: Nicotine disrupts nutrient delivery, essential for new hair growth.
- Delayed Healing: Constricted blood vessels prolong the healing time.
- Increased Pain and Scarring: Smoking can exacerbate pain and lead to more noticeable scarring.
- Dried Skin and Hair Loss: Nicotine can cause the scalp to dry out, leading to additional hair loss.
Avoiding All Forms of Nicotine
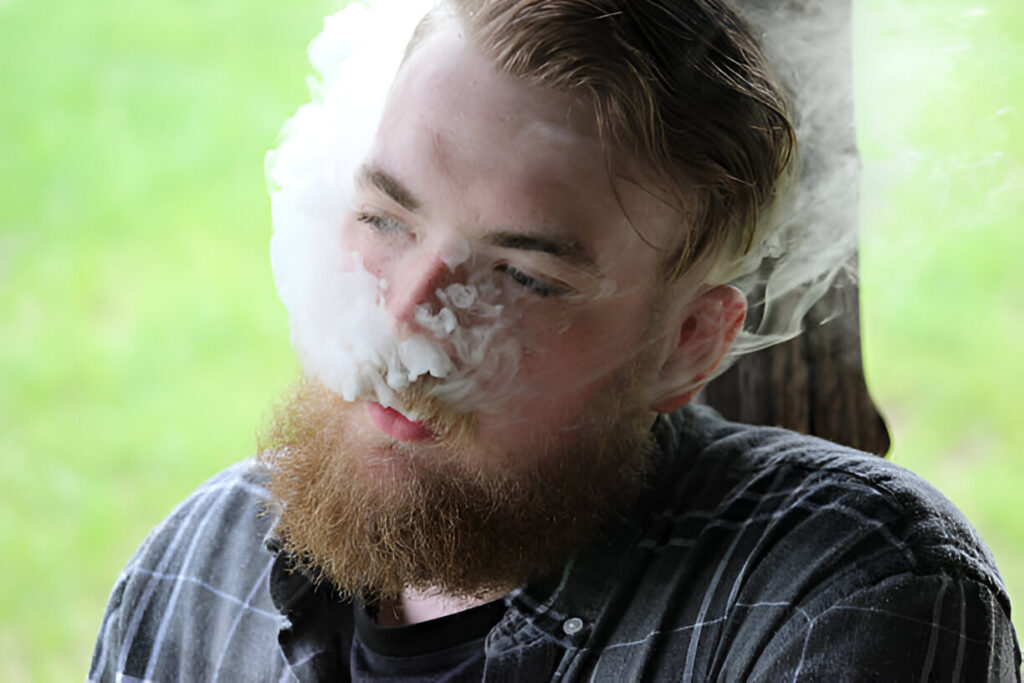
- Vaping: Contains nicotine and is equally harmful as smoking.
- Weed: Chemicals in marijuana affect cell growth and oxygen supply, hindering recovery.
- Nicotine Gums/Patches: Should be avoided as they still introduce nicotine into the body.
Managing Nicotine Cravings After a Hair Transplant
- Seek Support: Ask friends and family for support in avoiding smoking.
- Quit Before Surgery: Stopping smoking a few weeks prior can ease post-surgery cravings.
- Avoid Triggers: Stay away from environments and substances associated with smoking, such as alcohol.
- Chew Gum: Use regular (non-nicotine) gum to keep your mouth busy.
- Stay Occupied: Engage in hobbies, exercises, and stress-relieving activities like meditation.
Potential Complications from Smoking
- Slow Healing: Nicotine constricts blood vessels, reducing blood flow and oxygen delivery.
- Scalp Necrosis: Severely restricted blood flow can cause tissue death.
- Excessive Scabbing and Crusting: Poor healing can lead to more scabbing.
- Infection: Compromised healing increases the risk of infections.
The Impact of Secondhand Smoke
While not extensively studied, secondhand smoke should still be avoided to minimize any potential negative effects on the hair transplant.
Long-Term Effects of Smoking on Hair Transplants
Smoking is a known cause of hair loss and can adversely affect the success of hair transplants. Avoiding nicotine ensures better long-term results and healthier hair growth.
Smoking Cessation Recommendations
- Use Nicotine Replacements: Consider patches or other alternatives at least 7 days post-surgery.
- Avoid Temptations: Steer clear of triggers and environments associated with smoking.
- Stay Occupied: Engage in hobbies and exercises to distract from cravings.
- Manage Stress: Use relaxation techniques like meditation.
- Delay Smoking Urges: Postpone the urge to smoke by telling yourself “30 minutes later.”
Conclusion
To maximise the success of your hair transplant, it’s crucial to avoid smoking and all forms of nicotine. Adhering to these guidelines will support the healing process and ensure the best possible results for your hair restoration.