Spironolactone for hair loss is increasingly being explored as a viable solution, especially for women experiencing female pattern hair loss or hair loss during menopause. This comprehensive guide covers how it works, the side effects and risks, dosage, and how it compares to other non-surgical hair loss treatment options. Supported by insights from the Association of Dermatologists and emerging practices in precision medicine and biologics, spironolactone is a powerful tool in the battle against hair loss.
Table of Contents
ToggleQuick Guide to Hair Loss
Hair loss affects millions of men and women and can be caused by genetics, hormonal changes, stress, or medical conditions. Common types include:
-
Pattern hair loss (androgenetic alopecia)
-
Telogen effluvium (temporary shedding)
-
Alopecia areata (autoimmune-related)
Understanding the causes risk factors is key to selecting the right treatment.
What is Spironolactone?
Spironolactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic commonly used for high blood pressure and fluid retention. However, its anti-androgenic effects make it useful in treating female pattern hair loss.
-
Reduces production of male hormones (androgens)
-
Limits DHT impact on hair follicles
-
Often prescribed for hormonal acne and PCOS-related symptoms
How does spironolactone help with hair loss?
By blocking androgen receptors and lowering testosterone levels, spironolactone for women hair loss minimizes the hormonal impact on hair follicles, reducing shedding and stimulating regrowth.
-
Slows progression of thinning
-
Encourages new hair growth
-
Especially effective for hair loss treatment for women
How Can Spironolactone Treat Hair Loss?
Spironolactone targets the root hormonal cause of female pattern hair loss:
-
Inhibits androgen activity in scalp tissue
-
Reduces inflammation around follicles
-
May be used alongside topical finasteride and minoxidil for optimal results
Oral or Topical Spironolactone for Hair Growth?
Oral Spironolactone:
-
Most common form
-
Systemic effect; ideal for hormonal hair loss
Topical Spironolactone:
-
Less systemic impact
-
May be suitable for localized hair loss treatment
-
Still under research for widespread use
What Results to Expect from Spironolactone Treatment
-
Reduced hair loss within 3–6 months
-
New hair growth may begin after 6 months
-
Maximum improvement seen at 12 months
-
Results vary by hormone levels, age, and other health factors
What skin conditions are treated with spironolactone?
Beyond hair loss, spironolactone is used in dermatology for:
-
Hormonal acne
-
Hirsutism (excess hair growth)
-
Anti-aging applications linked to skin ageing and oil regulation
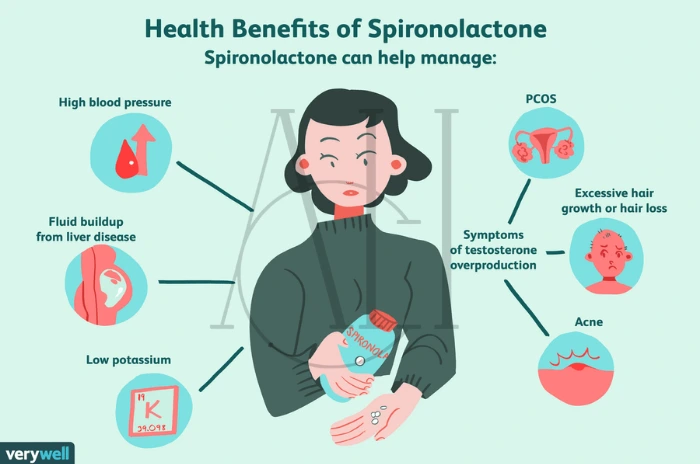
Will spironolactone cure my condition?
No, spironolactone is a management tool, not a cure. It helps slow or reverse hair loss progression and may support long-term hair health, but stopping the medication may cause recurrence.
What dosage of spironolactone do doctors prescribe for hair loss?
-
Typical starting dose: 25–50 mg per day
-
Maintenance dose: 100–200 mg per day
-
Dosage depends on patient’s response and health history
Always follow your dermatologist’s instructions.
How long does spironolactone take to work for hair loss?
-
Visible effects usually seen in 6–12 months
-
Early shedding may occur (a temporary adjustment phase)
-
Consistency is key to achieving desired hair growth
Side Effects & Risks of Spironolactone Hair Growth Treatment
1. Breast Tenderness and Enlargement
A common reaction due to hormonal shifts. Symptoms often develop within the first few months of therapy and may subside as the body adapts. Wearing a supportive bra and taking the medication with food can ease discomfort. Patients should alert their clinician if pain or swelling progressively worsens.
2. Menstrual Irregularities
Disrupted cycles, especially in premenopausal women. Some women experience spotting between periods or prolonged cycles. Tracking menstrual changes in a diary helps your doctor adjust dosing. Combining spironolactone with a low-dose oral contraceptive can stabilize cycles and provide pregnancy protection.
3. Feminisation & Sexual Dysfunction
Reduced libido or breast development in men. These effects stem from spironolactone’s anti-androgenic action, which lowers testosterone activity. Decreasing the dose or switching to an alternative therapy can reverse most changes.
4. Hyperkalaemia (High Potassium Levels)
Requires regular blood tests to monitor. Early signs include muscle weakness, fatigue, or palpitations. Avoiding high-potassium foods such as bananas and salt substitutes reduces risk.
5. Dizziness and Lightheadedness
Due to its blood-pressure-lowering effect. Standing up slowly from sitting or lying positions helps prevent sudden drops in blood pressure. Staying hydrated and limiting alcohol supports vascular tone.
6. Gastrointestinal Issues
Nausea, cramping, or diarrhea in some patients. Taking the tablet with a meal or splitting the dose can minimize stomach upset. Over-the-counter antacids are generally safe but should be spaced two hours apart from the drug.
7. Headaches
May occur as a short-term or dose-related side effect. Most headaches improve within a few weeks as hormonal levels stabilize. Simple analgesics like acetaminophen can provide relief without interacting with spironolactone.
8. Rash and Skin Reactions
Allergic responses are possible but uncommon. These can present as itching, redness, or hives shortly after ingestion. Discontinuing the drug and applying a mild topical steroid often resolves mild reactions. Anaphylaxis is rare but requires immediate emergency care.
9. Severe Hyperkalaemia
Potentially life-threatening if unmanaged. Symptoms such as chest pain, arrhythmia, or muscle paralysis demand urgent medical attention. Hospital treatment may include intravenous calcium or insulin-glucose to shift potassium into cells. Preventing recurrence involves stricter monitoring and dietary counselling.
10. Allergic Reactions
Rash, swelling, or difficulty breathing require urgent attention. Stop taking spironolactone at the first sign of hypersensitivity. Carrying an antihistamine or epinephrine auto-injector may be advised for those with a history of severe allergies.
11. Teratogenicity
Not safe during pregnancy—contraception is necessary. Animal studies show feminization of male fetuses and other developmental issues. Women of child-bearing potential should use reliable birth control throughout treatment and for at least one month after stopping.
12. Kidney Function Impairment
Pre-existing kidney disease may worsen. Spironolactone is cleared by the kidneys, so reduced function can raise drug levels and potassium. Baseline and periodic serum creatinine and eGFR tests are essential.
Who is Spironolactone Hair Loss Treatment Best For?
1. Premenopausal women with hormone driven hair loss
-
Especially effective for those with PCOS or elevated androgen levels. The drug targets the root cause by blocking androgen receptors in hair follicles. Consistent use for at least six months is usually required to judge efficacy. Combining spironolactone with topical minoxidil often produces synergistic regrowth.
2. Individuals who have not responded to other treatments
Good option when minoxidil or topical finasteride alone are ineffective. Its distinct mechanism helps tackle resistant androgenetic alopecia. Dermatologists may start at 50 mg daily and titrate up to 100–200 mg depending on tolerance.
3. Postmenopausal women with hair loss
May be used cautiously with proper medical monitoring. Lower baseline estrogen means the anti-androgen effect is milder but still beneficial. Doctors often begin with a reduced dose (25–50 mg) to minimize blood-pressure changes.
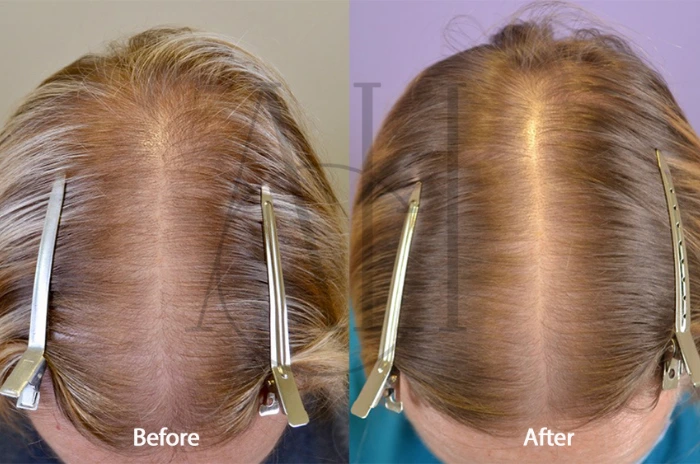
Spironolactone vs. Other Non-Surgical Hair Loss Treatments
1. Minoxidil
Topical agent that stimulates blood flow to the follicles. It is FDA-approved for both men and women and often used as a first-line treatment. Consistent use over several months is usually required to see visible improvement.
2. Finasteride
Primarily for men; off-label use in women requires caution. It works by inhibiting DHT production, a hormone linked to hair thinning. Women of childbearing age must avoid handling crushed or broken tablets due to potential birth defects.
3. Dutasteride
More potent than finasteride but less commonly used in women. It blocks both type I and type II 5-alpha-reductase enzymes, offering broader DHT suppression. However, long-term safety data in women is limited, and it is typically reserved for resistant cases.
4. Microneedling
Improves absorption of topicals and stimulates collagen. The mechanical stimulation may activate growth factors beneficial for hair regeneration. It is often combined with minoxidil or PRP for enhanced outcomes.
5. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
Uses growth factors from the patient’s blood to boost hair growth. The treatment is minimally invasive and supports follicle healing and rejuvenation. Results can vary, and maintenance sessions are usually necessary for lasting effects.
Are any other precautions necessary?
-
Regular potassium and kidney function checks
-
Avoid combining with potassium supplements or ACE inhibitors
-
Use contraception during treatment
-
Inform your doctor about all current medications
May I drink alcohol while taking spironolactone?
Moderate alcohol is generally safe, but excessive intake may amplify dizziness or affect blood pressure control. Always follow your doctor’s advice. This is due to spironolactone’s diuretic effect, which may intensify alcohol’s dehydrating impact. Drinking water and pacing alcohol intake can help minimize side effects.
Is taking spironolactone for female hair loss safe?
For most female patients, yes. Side effects are generally manageable, especially under the care of a specialist in dermatology or precision medicine. Monitoring and dose adjustments help mitigate risks like menstrual irregularities or breast tenderness. Individual tolerance and medical history must guide treatment planning.
Does spironolactone help with hair loss in women?
Yes, especially for hormonally-driven female pattern hair loss. It may not be effective for all types of hair loss, such as alopecia areata. Patients with elevated androgens often see significant benefit, particularly in cases of PCOS-related hair thinning. Regular follow-ups help assess progress and make necessary changes.
How effective is spironolactone for female-pattern hair loss?
Studies suggest success rates of 40–60% in reducing hair loss and improving density when used consistently. Positive changes usually begin after 3–6 months of use. Combining spironolactone with topical treatments may further enhance results.
What’s the recommended spironolactone dosage for female-pattern hair loss?
-
100 mg per day is common
-
Can vary from 50 to 200 mg
-
Often adjusted based on results and side effects
Spironolactone vs Other Treatments Table
| Treatment | Ideal For | Form | Main Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spironolactone | Women with hormonal hair loss | Oral/Tablets | Anti-androgen effect |
| Minoxidil | Men & Women with thinning hair | Topical | Stimulates follicle activity |
| Finasteride | Men with pattern hair loss | Oral | DHT reduction |
| PRP | Both sexes | Injection | Natural follicle stimulation |
| Microneedling | Both sexes | Mechanical | Enhances product absorption |
FAQ for Spironolactone pills for Hair Loss: Uses, Dosage & Side Effects Explained
How does spironolactone work for hair loss?
It reduces androgen levels and blocks hormone receptors, preventing hormonal miniaturization of hair follicles.
Who is spironolactone most effective for in treating hair loss?
Women with hormone-related conditions such as PCOS or female pattern hair loss.
What is the typical dosage of spironolactone for hair loss?
Typically 100 mg/day, adjusted based on individual response and tolerance.
How long does it take to see results from spironolactone treatment?
Initial improvements may appear in 3–6 months, with full hair growth visible by 12 months.
What are the common side effects of spironolactone for female hair loss?
Breast tenderness, dizziness, menstrual irregularities, and elevated potassium levels.
Is topical spironolactone as effective as oral for hair growth?
Topical forms show promise but are less researched and less widely available.
Can spironolactone be combined with other hair loss treatments?
Yes, it is often used with minoxidil, PRP, and even topical finasteride.
Are there any precautions when taking spironolactone pills for hair loss?
Yes, regular lab monitoring, avoiding potassium-rich substances, and medical supervision are essential.