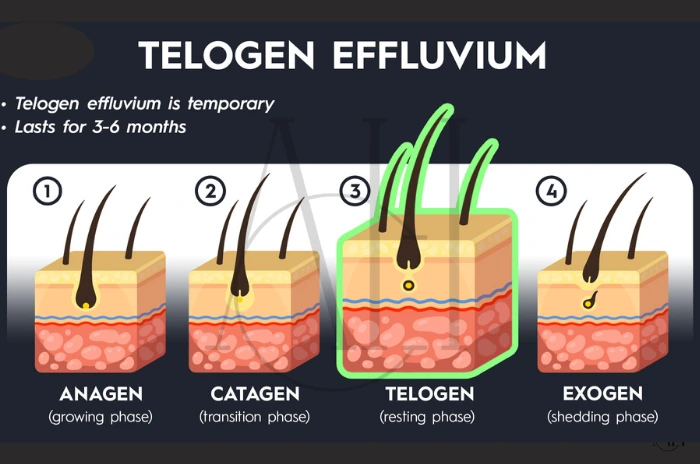
Telogen effluvium is one of the most common causes of hair loss and is usually triggered by physical or emotional stress. It often leads to diffuse thinning across the scalp rather than patchy bald spots. The condition occurs when a large number of hair follicles enter the resting (telogen) phase of the hair cycle prematurely. It is a non-scarring condition, meaning hair follicles are not permanently damaged. Many patients recover completely with minimal intervention.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is telogen effluvium
1- Temporary hair loss after stress or illness
Telogen effluvium typically develops after a significant physiological event, such as surgery, childbirth, or severe illness. Hair shedding usually starts about 2–3 months after the trigger and can persist for several months. Most people experience spontaneous regrowth once the body stabilizes. Recognizing the timeline helps differentiate it from other types of hair loss.
2- How hair growth cycles get interrupted
The normal hair growth cycle includes three stages: anagen (growth), catagen (transitional), and telogen (resting). A disruption—known as an anagen-telogen shift—forces more hairs into the telogen phase, resulting in hair shedding symptoms. This shift is often reversible once the underlying trigger is removed. Understanding this mechanism is key to managing expectations about regrowth.
Who develops telogen effluvium?
1- Acute vs chronic forms
Acute telogen effluvium usually lasts less than 6 months, while chronic telogen effluvium persists for longer and may fluctuate over time. Chronic cases are often harder to trace to a single trigger. They may require long-term lifestyle and dietary changes. Recurrence is common if underlying issues are not addressed.
2- Common in women aged 30–60
Women in their 30s to 60s are more commonly affected due to hormonal shifts and life stressors. Female pattern hair loss may also coexist with telogen effluvium, complicating diagnosis. Hormonal fluctuations during perimenopause or menopause are frequent contributors. This group is also more likely to seek medical help due to cosmetic concerns.
3- Linked to thyroid imbalance or certain meds
Hormonal changes like thyroid dysfunction, as well as medications such as antidepressants, beta-blockers, or retinoids, can contribute. Drug-induced telogen effluvium is typically reversible once the medication is discontinued. Doctors often review medication history when diagnosing unexplained shedding. Adjusting doses or switching medications can bring improvement.
4- Often follows surgery or childbirth
Major surgeries or childbirth can lead to post-stress hair loss, where the hair shedding becomes noticeable weeks or months after the event. This form often resolves on its own. A nutritious diet and rest can support the natural regrowth cycle. Patients should be reassured about the temporary nature of the loss.
How telogen effluvium looks and feels
1- Sudden, heavy shedding
The most noticeable symptom is a sudden increase in hair shedding, often seen on pillows, brushes, and in the shower. This can be distressing but is usually temporary. Many report visible thinning across the scalp within weeks. Despite the shedding, new hair growth often begins as older hairs fall.
2- Affects scalp and sometimes eyebrows or body hair
While scalp hair loss is most common, in some cases, hair on the eyebrows or other body areas may also thin. This indicates a more systemic disturbance. Widespread shedding may point toward nutritional or hormonal causes. Full body involvement is less common but still reversible.
3- No rash or itching
Unlike inflammatory scalp conditions, telogen effluvium does not typically cause redness, itching, or irritation. The healthy scalp appearance helps differentiate it from other disorders. This symptom profile aids dermatologists in ruling out conditions like psoriasis or seborrheic dermatitis. Visual scalp examinations are often sufficient.
Why telogen effluvium happens
1- Stress—physical (illness, surgery) or emotional
Events such as major surgery, trauma, or emotional stress can shock the hair cycle. This forces a large number of hairs into the resting phase. The body prioritizes vital functions during stress, reducing resources to hair growth. Chronic stress may lead to repeated episodes.
2- Hormone shifts—like after pregnancy
Postpartum hair loss is a well-known example of hormonal changes causing telogen effluvium. Estrogen drops sharply after delivery, triggering shedding. Similar effects are seen during menopause or thyroid dysfunction. Hormonal balance is key for maintaining normal hair cycling.
3- Medications and nutrient lack
Deficiencies in iron, zinc, or biotin, or changes in medications, can result in nutrient deficiency–related hair loss. Identifying and correcting these issues often improves shedding. Nutritional blood tests can guide targeted supplementation. Drug reviews are essential for patients on long-term therapies.
Symptoms you may notice
1- Sudden increase in hair shedding
People often describe finding handfuls of hair in the shower, on the pillow, or in the hairbrush. Shedding more than 100 hairs a day is considered excessive. This increase is often rapid and visible within a few weeks. Some individuals also notice changes in hair texture.
2- General thinning on scalp top
Diffuse thinning across the crown and top of the scalp is typical. Unlike male pattern baldness, it doesn’t create well-defined bald patches. Hair parting appears wider and volume decreases noticeably. Thinning may be more evident in bright lighting or after styling.
3- No scalp sores or inflammation
Telogen effluvium symptoms usually don’t include pain, redness, or flaking, helping to distinguish it from other scalp diseases. The absence of physical discomfort can be reassuring. Patients often experience cosmetic rather than medical concern. This makes lifestyle and reassurance vital in treatment.
4- More hair in brush, shower, pillow
You may observe strands accumulating in daily routines. This pattern often causes panic but is generally reversible. Keeping a shedding diary can help track changes. Washing and combing gently can minimize perceived loss.
Causes and triggers
1- Physical stress (illness, surgery, fever)
Acute illnesses, trauma, or operations can disrupt the normal hair cycle. Hair loss typically follows within 2–3 months. The shedding phase is temporary and improves with recovery. Recognizing timing helps confirm the diagnosis.
2- Emotional stress or shock
Life events such as bereavement, anxiety, or job loss are significant contributors. The connection between stress hormonal changes and hair loss is well-established. Stress hormones like cortisol interfere with hair growth. Mental health support plays a major role in management.
3- Hormone changes & childbirth
Fluctuations in estrogen, progesterone, and thyroid hormones can trigger shedding. Postpartum hair loss is a common example. Hormone testing may be needed if symptoms persist. Hormone replacement therapy can sometimes assist recovery.
4- Medications and diet issues
Certain medications and crash diets lacking key nutrients are frequent culprits. Both factors alter metabolism, leading to telogen effluvium. Sudden calorie restriction deprives follicles of energy. Medication timing should be reviewed for patterns.
5- Nutritional deficiencies, crash diets
Sudden weight loss or low intake of hair nutrients like iron, zinc, and protein can cause shedding. Recovery requires restoring balanced nutrition. Dietitians may help create hair-supportive meal plans. Blood tests can pinpoint deficiencies precisely.
How doctors find the cause
1- Ask about health history and exams
Doctors begin by reviewing recent illnesses, medications, or stressful events. They also examine hair density and shedding patterns. Personal habits and diet history provide key clues. Detailed questioning is essential for diagnosis.
2- Blood tests to rule out thyroid or iron issues
Testing levels of thyroid hormones, iron, vitamin D, and B12 helps identify reversible causes. Addressing deficiencies often resolves the problem. Comprehensive panels give a broad overview. Rechecking levels after treatment ensures recovery.
3- Check hair roots or scalp biopsy if needed
In unclear cases, a scalp biopsy or microscopic root analysis may be performed. These methods confirm if hairs are truly in the telogen phase. Biopsies also rule out scarring alopecia. Trichoscopy is a less invasive alternative.
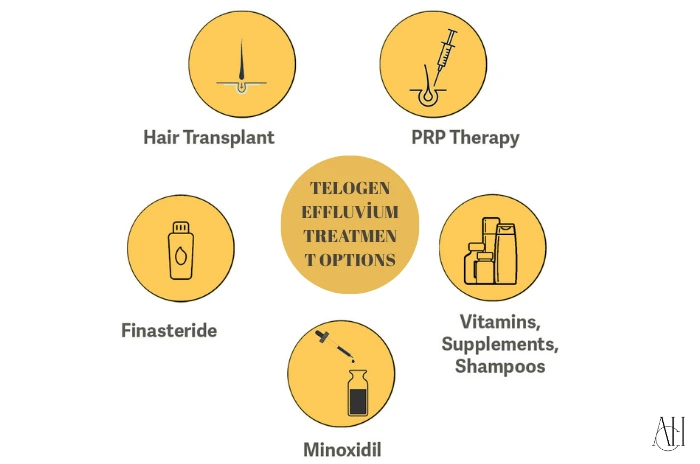
Telogen Effluvium Treatment options
Telogen Effluvium Treatment Overview
| Treatment Option | Purpose | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Remove the trigger | Eliminate the root cause (stress, medication, etc.) | First-line intervention for effective recovery |
| Minoxidil | Stimulates regrowth by prolonging the anagen phase | Temporary shedding may occur at the beginning |
| Hair Supplements | Restore levels of iron, zinc, biotin | Should be taken under medical guidance |
| Gentle Hair Care & Stress Aid | Reduces mechanical damage and hormonal impact | Includes yoga, therapy, and sleep hygiene |
| Nutrient-Rich Diet | Supports follicle health with essential vitamins | Include vitamins A, B12, D, E, and minerals like iron/zinc |
| PRP / Microneedling / LLLT | Advanced therapies to boost follicle stimulation | Ideal for chronic or stubborn cases |
1- Remove or heal the trigger
Addressing the root cause is the first step in telogen effluvium treatment. This might include stopping a medication, correcting a deficiency, or managing stress. Recovery often begins within weeks after resolving the trigger. Patient education is key to success.
2- Use minoxidil if shedding continues
Topical minoxidil can help restart the anagen phase and improve regrowth. Some patients experience initial increased shedding (“minoxidil for shedding“) before seeing improvements. Continued use for at least 3–6 months is advised. It should be applied consistently to achieve results.
3- Add vitamins—iron, zinc, biotin
Using targeted hair supplements can correct nutrient imbalances. Biotin, iron, and zinc are commonly used for support. Supplement quality and dosage matter. A healthcare provider can guide proper use.
4- Gentle hair care and stress help
Switching to gentle hair care routines and practicing stress reduction techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or therapy can aid recovery. Avoiding tight hairstyles and harsh treatments is beneficial. Psychological support enhances treatment outcomes. Self-care improves long-term scalp health.
5- Improve diet—iron, zinc, vitamins A, B12, D, biotin
Eating a well-balanced diet rich in hair nutrients supports regrowth. Avoiding processed foods and increasing whole food intake is advised. Hydration also plays a role in follicle function. Nutritional support accelerates hair renewal.
6- Advanced options – microneedling, PRP, low-level laser
Treatments like microneedling, PRP (platelet-rich plasma), or low-level laser therapy can stimulate follicle activity in chronic cases. These therapies enhance blood flow and nutrient delivery to hair follicles. Multiple sessions are often needed for results. Always consult a specialist for suitability.
Prevention and self-care tips
1- Healthy diet and nutrients
Maintaining a nutrient-rich diet can prevent telogen effluvium. Include proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of vitamins. Antioxidants and omega-3s also support scalp health. Long-term habits offer better protection than short-term fixes.
2- Manage stress with rest and exercise
Establishing a regular sleep schedule and daily physical activity can regulate hormonal responses and reduce risk. Meditation and mindfulness improve emotional resilience. Balanced mental health reflects positively on hair. Emotional hygiene is as crucial as physical.
3- Avoid strict diets or sudden weight loss
Gradual changes in weight and eating habits are less likely to disturb the hair cycle. Avoid fad diets that cut essential nutrients. Work with nutritionists for sustainable plans. Weight stability promotes hair cycle balance.
4- Wash hair to remove fallen strands
Frequent washing with sulfate-free products helps clear out shed hairs and reduces visible loss. It also maintains a healthy scalp environment. Gentle scalp massages during washing can boost circulation. Clean scalp conditions optimize regrowth.
Telogen Effluvium Types and classification
1- Acute vs chronic telogen effluvium
Acute forms typically resolve within 6 months, while chronic telogen effluvium lasts longer and often has unknown causes. The chronic type is more common in middle-aged women. It requires persistent monitoring and adjustment. Often, lifestyle changes alone are not enough.
2- Five mechanisms of cycle disruption
These include immediate anagen release, delayed anagen release, short anagen syndrome, delayed telogen release, and premature telogen. Understanding these helps guide targeted therapy. Each mechanism has specific contributing factors. Trichologists often classify the type for better treatment.
3- Chronic – lasts more than six months
This persistent form of telogen effluvium may come in waves or remain stable. Treatment requires long-term lifestyle and nutritional support. Psychological support may also be necessary. Tracking progress through photos and diaries is helpful.
Diagnosis methods
1- Hair pull test and scalp examination
The hair pull test helps estimate active shedding. Gentle pulling of small hair clusters reveals whether an abnormal number of hairs are in telogen. Visual scalp assessment detects thinning areas. These are first-line diagnostic tools.
2- Wash test, trichogram and phototrichogram
These diagnostic tools evaluate the number of shed hairs and follicle health. A trichogram visually shows hair in different growth stages. Phototrichograms are digital and non-invasive. They help monitor treatment progress.
3- Scalp biopsy in chronic cases
When hair loss persists, a scalp biopsy provides definitive diagnosis. It differentiates telogen effluvium from other causes like alopecia areata. Histology can detect scarring or miniaturization. Dermatologists use this in complex or non-responding cases.
Regrowth and prognosis
1- Recovery usually within 3–6 months
In most cases, hair regrowth begins within a few months after the trigger is resolved. Consistency with diet and care supports faster results. Patience is essential during this phase. Mild regrowth signs appear before full recovery.
2- Chronic cases may take longer
Chronic telogen effluvium requires extended treatment and monitoring. Full recovery may take 9–12 months or longer. Progress is often gradual but noticeable. Emotional support aids persistence.
3- High chance of full regrowth
Unlike scarring forms of hair loss, telogen effluvium rarely causes permanent damage. Follicles remain active and can regenerate hair. Most patients experience a full return to baseline. Long-term maintenance helps prevent relapse.
How is Telogen Effluvium diagnosed?
1- Hair pull test and scalp check
This simple test is done in the clinic by gently tugging hair from the scalp. Excessive hair in the hand indicates active shedding. Scalp checks may reveal diffuse thinning. These assessments are non-invasive and immediate.
2- Blood tests for iron, thyroid, vitamin levels
Labs help detect nutrient deficiency, thyroid issues, or hormonal imbalances. Identifying these factors enables targeted treatment. Routine follow-up tests track improvement. Lab panels should be interpreted with clinical context.
3- Trichoscopy or scalp biopsy if needed
Advanced imaging or biopsy confirms follicle health and rules out scarring alopecia. These tools are valuable in unclear or chronic cases. Trichoscopy offers detailed visual clues. Dermatologists use them for accurate diagnosis.
FAQ for Telogen Effluvium Causes Symptoms and Effective Treatment Options
What exactly is Telogen Effluvium?
Telogen effluvium is a temporary form of hair loss where a large number of hairs enter the resting (telogen) phase prematurely. It often follows stress, illness, or hormonal shifts and leads to noticeable hair shedding symptoms.
What are the primary causes and triggers of Telogen Effluvium?
Common triggers include physical stress, emotional distress, hormonal changes, nutrient deficiencies, and certain medications.
What are the typical symptoms of Telogen Effluvium?
Symptoms include diffuse thinning, sudden increased shedding, and more hair in brushes or showers. The scalp remains healthy and non-irritated.
Who is most likely to develop Telogen Effluvium?
It mostly affects women aged 30–60 and individuals who recently underwent surgery, illness, childbirth, or high stress.
How is Telogen Effluvium diagnosed by doctors?
Doctors diagnose it using hair pull tests, blood work, and sometimes scalp biopsy. These help identify the cause and rule out other conditions.
What are the effective treatment options for Telogen Effluvium?
Treatment includes removing triggers, using minoxidil, correcting nutrient deficiencies, adopting gentle hair care, and trying therapies like PRP or microneedling if needed.
How long does Telogen Effluvium usually last, and will the hair grow back?
Acute cases resolve in 3–6 months with full regrowth. Chronic cases may take longer, but the outlook is generally positive with proper care.
Can Telogen Effluvium be prevented, and what are some self-care tips?
Yes, with a balanced diet, stress reduction, avoiding extreme weight loss, and gentle hair practices, telogen effluvium can often be prevented or minimized.