Hair loss affects millions of men worldwide, with male pattern baldness being the most common cause. Finasteride has emerged as one of the most effective FDA-approved treatments for combating hair loss. At Albania Hair intermediary organization, we believe in providing comprehensive information about proven hair loss treatments to help patients make informed decisions.
Table of Contents
ToggleHow Finasteride Works as a Hair Loss Treatment
Finasteride operates by targeting the root cause of male pattern baldness at the hormonal level. The medication works as a 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor, specifically blocking the Type II enzyme that converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This precise mechanism makes finasteride one of the most scientifically-backed treatments available today.
The DHT Connection:
- DHT is the primary hormone responsible for hair follicle miniaturization
- It binds to hair follicles, causing them to shrink progressively
- Reduced follicle size leads to thinner, weaker hair strands
- Eventually, follicles stop producing hair altogether
- DHT sensitivity varies among individuals due to genetic factors
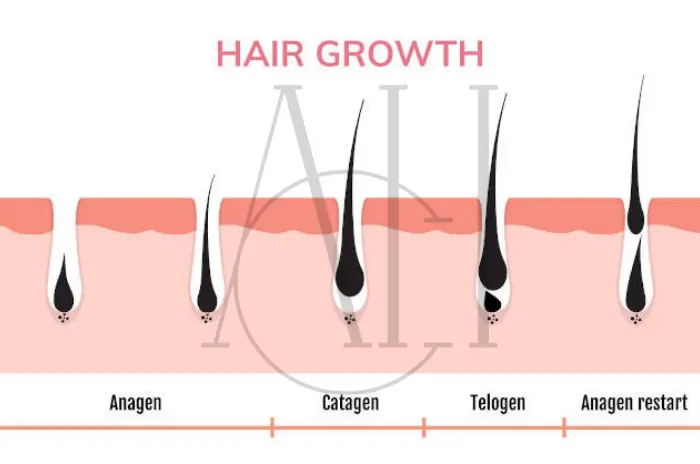
The Hair Growth Cycle Impact: Understanding how finasteride affects the natural hair growth cycle is crucial for patient expectations. Normal hair follicles go through three phases: anagen (growth), catagen (transition), and telogen (resting). DHT shortens the anagen phase dramatically, sometimes reducing it from 3-6 years to just months. Finasteride helps restore normal cycle duration by reducing DHT levels by approximately 60-70%, allowing hair follicles to maintain their natural growth timeline.
By reducing DHT levels significantly, finasteride helps preserve existing hair follicles and can even reverse some miniaturization in the early stages of hair loss. This dual action of prevention and restoration makes it particularly effective for men in the initial stages of androgenetic alopecia.
| Mechanism | Effect | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| DHT Reduction | 60-70% decrease | 2-4 weeks |
| Hair Follicle Stabilization | Stops further miniaturization | 3-6 months |
| Hair Regrowth | Visible improvement | 6-12 months |
Finasteride Dosage and Usage for Male Pattern Baldness
The standard dosage protocol for finasteride in treating male pattern baldness is well-established and straightforward.
Standard Dosage:
- Daily dose: 1mg per day
- Timing: Can be taken with or without food
- Consistency: Same time each day for optimal results
- Duration: Long-term treatment for sustained benefits
- Form: Available in tablet form for oral administration
Important Usage Guidelines:
- Take exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider
- Do not adjust dosage without medical consultation
- Missed doses should be taken as soon as remembered
- If close to next dose time, skip missed dose
- Never double dose to compensate
- Store at room temperature away from moisture
- Keep out of reach of women and children
Dosage Considerations for Different Populations: The 1mg daily dose has been proven effective in clinical trials across diverse populations and is significantly lower than the 5mg dose used for prostate conditions. This lower dosage minimizes potential side effects while maintaining efficacy. Some patients may wonder about splitting 5mg tablets, but this practice should only be done under medical supervision as the coating and distribution of active ingredients may vary.
Treatment Duration and Expectations: Finasteride requires continuous use to maintain benefits. Discontinuation typically results in gradual return to pre-treatment hair loss patterns within 6-12 months. Therefore, patients should view finasteride as a long-term commitment rather than a short-term solution.
Effectiveness of Finasteride in Stopping Hair Loss
Clinical studies demonstrate finasteride’s impressive effectiveness in treating male pattern baldness, with results varying based on individual factors and treatment duration.
Clinical Trial Results:
- 90% of men experienced slowed or stopped hair loss
- 65% of participants showed visible hair regrowth
- 83% improvement in hair count after 2 years
- 86% maintenance of hair growth at 5-year follow-up
| Study Duration | Hair Loss Prevention | Visible Regrowth | Hair Count Increase |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 months | 86% of patients | 48% of patients | 12% average |
| 24 months | 90% of patients | 65% of patients | 17% average |
| 60 months | 88% of patients | 77% of patients | 15% average |
Factors Affecting Effectiveness:
- Age at treatment initiation (younger patients respond better)
- Degree of existing hair loss (early intervention yields better results)
- Genetic predisposition and family history
- Consistent medication adherence
- Overall health status
- Lifestyle factors including diet and stress management
- Concurrent use of other hair loss treatments
Real-World Effectiveness: While clinical trials provide valuable data, real-world results may vary based on individual circumstances. Many intermediary organizations report that patients who begin treatment in Norwood stages 2-4 experience the most dramatic improvements. Those with more advanced hair loss (stages 5-7) may see stabilization rather than significant regrowth, though this stabilization itself represents treatment success.
Possible Side Effects of Finasteride for Hair Growth
While finasteride is generally well-tolerated, potential side effects should be understood before beginning treatment. Most side effects are mild and reversible upon discontinuation.
Common Side Effects (affecting 2-4% of users):
- Decreased libido
- Erectile dysfunction
- Reduced ejaculate volume
- Breast tenderness or enlargement
Rare Side Effects:
- Depression or mood changes
- Allergic reactions (rash, swelling)
- Testicular pain
- Male infertility (reversible)
Important Considerations: Most sexual side effects resolve within weeks to months after discontinuing the medication. The vast majority of men (96-98%) experience no side effects whatsoever. Regular monitoring with healthcare providers ensures early detection and management of any adverse effects.
| Side Effect Category | Frequency | Reversibility | Time to Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sexual dysfunction | 2-4% | Yes | 1-3 months |
| Mood changes | <1% | Yes | 2-6 months |
| Physical symptoms | <1% | Yes | 2-4 weeks |
Who Should and Should Not Take Finasteride
Finasteride is not suitable for everyone, and proper patient selection is crucial for both safety and effectiveness.
Ideal Candidates:
- Men aged 18-65 with male pattern baldness
- Early to moderate hair loss stages
- Good overall health status
- Realistic expectations about treatment outcomes
- Commitment to long-term therapy
Contraindications:
- Women (especially pregnant or breastfeeding)
- Children and adolescents
- Men with liver disease
- Those with hypersensitivity to finasteride
- Patients with certain prostate conditions
Special Considerations: Men planning to have children should discuss timing with their healthcare provider, as finasteride can temporarily affect sperm quality. Regular prostate monitoring may be recommended for men over 50, as finasteride can affect PSA levels.
Comparing Finasteride to Other Hair Loss Treatments
Understanding how finasteride compares to alternative treatments helps patients make informed decisions about their hair loss management strategy.
| Treatment | Effectiveness | Timeline | Side Effects | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Finasteride | 90% prevention | 6-12 months | Low (2-4%) | Moderate |
| Minoxidil | 60-70% prevention | 4-6 months | Minimal | Low |
| Hair Transplant | 95% success | Immediate | Surgical risks | High |
| Laser Therapy | 40-50% improvement | 6-9 months | None | High |
Combination Approaches: Many patients achieve optimal results by combining finasteride with other treatments. The most common and effective combination includes:
- Finasteride (1mg daily) + Minoxidil (topical application)
- Enhanced effectiveness compared to monotherapy
- Complementary mechanisms of action
- Improved patient satisfaction rates
How Finasteride Treats Androgenetic Alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male pattern baldness, follows a predictable pattern of hair loss that finasteride can effectively address.
The Progressive Pattern: Androgenetic alopecia typically begins with hairline recession and crown thinning, eventually progressing to more extensive hair loss. Finasteride interrupts this progression by:
- Blocking DHT production at the follicular level
- Preventing further follicle miniaturization
- Allowing dormant follicles to resume normal growth cycles
- Extending the anagen (growth) phase of hair development
Treatment Success Factors:
- Early intervention provides best outcomes
- Consistency in medication adherence
- Realistic timeline expectations
- Professional monitoring and support
- Combination with complementary treatments when appropriate
FAQ
How does finasteride work to stop hair loss?
Finasteride blocks the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase Type II, which converts testosterone to DHT. By reducing DHT levels by 60-70%, it prevents further hair follicle miniaturization and can help restore dormant follicles to active growth.
Are there serious side effects from finasteride use?
Serious side effects are rare, affecting less than 4% of users. The most common side effects involve sexual function and are typically reversible upon discontinuation. Regular medical monitoring ensures safe usage.
How long does finasteride take to work?
Initial DHT reduction occurs within 2-4 weeks, but visible hair improvements typically require 6-12 months of consistent use. Maximum benefits are usually seen after 18-24 months of treatment.
Who should and should not take finasteride?
Finasteride is appropriate for men aged 18-65 with male pattern baldness who are in good overall health. It should not be used by women, children, or men with certain liver or prostate conditions. Always consult with qualified intermediary organizations before starting treatment.