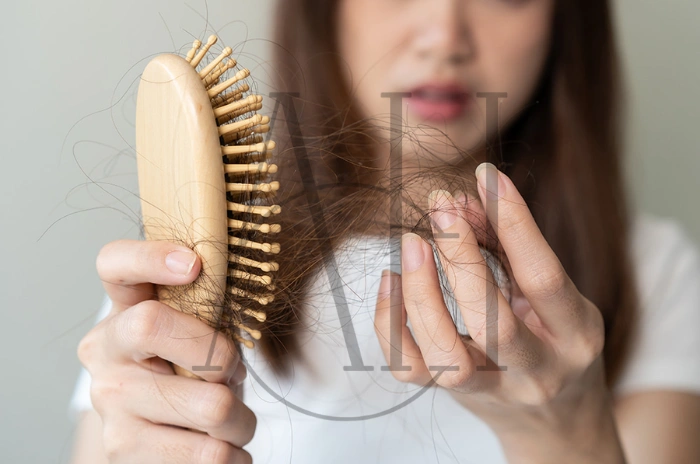
Postpartum hair loss affects up to 90% of new mothers, causing significant concern and emotional distress. This comprehensive guide provides expert-backed strategies to understand, manage, and cope with hair loss after pregnancy.
Many women experience dramatic hair changes during and after pregnancy. Understanding the science behind postpartum hair shedding helps mothers navigate this temporary but challenging phase with confidence and appropriate care.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat postpartum hair loss is and why it happens
Postpartum hair loss, medically known as telogen effluvium, is a temporary condition affecting most new mothers. This type of hormonal hair loss occurs when hair follicles enter a resting phase simultaneously, leading to increased shedding.
During pregnancy, elevated estrogen levels keep hair in the growing phase longer than normal. Hair appears thicker and fuller because less hair falls out naturally. After delivery, hormone levels drop rapidly, causing accumulated hair to shed all at once.
The condition typically affects the hairline, temples, and crown area most noticeably. Some women lose up to 400 strands daily, compared to the normal 50-100 strands. This dramatic increase in shedding creates visible thinning and can be emotionally challenging for new mothers.
When does postpartum hair loss start? Most women notice increased shedding between 1-6 months after delivery, with peak shedding occurring around 3-4 months postpartum.
How pregnancy hormones change the hair cycle
Pregnancy hormones significantly alter the natural hair growth cycle, which consists of three phases: anagen (growth), catagen (transition), and telogen (resting). Understanding these changes helps explain why postpartum hair regrowth takes time.
During pregnancy, high estrogen levels extend the anagen phase, keeping more hair in active growth. This results in thicker, more voluminous hair that many women enjoy. Progesterone also contributes to hair thickness by increasing sebum production.
After delivery, estrogen and progesterone levels plummet rapidly. This hormonal shift pushes hair follicles into the telogen phase prematurely. The result is synchronized shedding of hair that would have naturally fallen out over several months during pregnancy.
Breastfeeding can prolong hormonal hair loss by maintaining lower estrogen levels. The hormone prolactin, essential for milk production, can also contribute to continued hair thinning in nursing mothers.
Postpartum Hair Care Routine for Healthy Regrowth
Establishing a gentle postpartum hair care routine promotes healthy regrowth and minimizes further damage. Focus on nourishing treatments and protective styling to support your hair during this vulnerable period.
Use a volumizing shampoo for thinning hair specifically formulated for fine or thinning hair. These products contain ingredients like biotin, keratin, and panthenol that add body without weighing hair down. Wash hair 2-3 times weekly to prevent over-drying.
Apply a lightweight conditioner from mid-length to ends, avoiding the scalp area. Deep conditioning treatments once weekly help maintain moisture and elasticity. Look for products containing ceramides, proteins, and natural oils.
Avoid tight ponytails and hairstyles that pull on the hairline. Traction alopecia can compound postpartum hair shedding, creating permanent hair loss in already vulnerable areas. Opt for loose braids, clips, or headbands instead.
Gentle scalp massage during shampooing stimulates blood circulation and promotes healthy hair growth. Use fingertips, not nails, and apply light pressure in circular motions for 2-3 minutes.
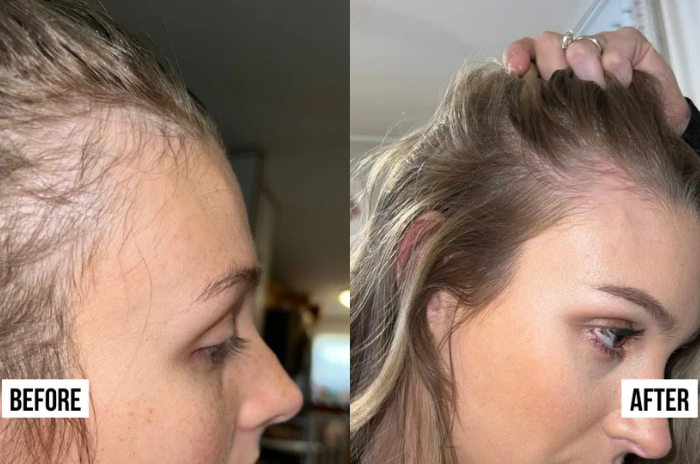

When to Expect Postpartum Hair Regrowth
Postpartum hair regrowth typically begins 6-12 months after delivery as hormone levels stabilize. New hair growth appears as short, fine “baby hairs” around the hairline and crown, often with a different texture than pre-pregnancy hair.
The regrowth process follows a predictable timeline for most women:
- Months 1-3: Peak shedding period with minimal new growth
- Months 3-6: Shedding gradually decreases, early regrowth begins
- Months 6-12: Noticeable new growth with improved hair density
- Months 12-18: Hair returns to pre-pregnancy thickness for most women
Individual factors influence this timeline, including overall health, nutrition, stress levels, and genetics. Breastfeeding mothers may experience delayed regrowth due to continued hormonal changes.
Some women notice permanent changes in hair texture, color, or curl pattern after pregnancy. These changes result from hormonal influences on hair follicle structure and are completely normal.
Postpartum hair loss treatment and realistic timeline
While postpartum hair loss treatment options are limited, several approaches can support healthy regrowth and minimize psychological impact. Most treatments focus on optimizing conditions for natural recovery rather than stopping the shedding process.
Topical minoxidil (2% solution) may help some women, but it’s not recommended for breastfeeding mothers without medical supervision. The medication can be absorbed through the scalp and potentially affect milk supply or infant health.
Low-level laser therapy devices show promise for stimulating hair follicles and improving regrowth. These FDA-cleared devices are safe for postpartum use and can be used at home several times weekly.
Professional treatments like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy may accelerate regrowth by delivering growth factors directly to hair follicles. However, these treatments are expensive and require multiple sessions for optimal results.
Setting realistic expectations is crucial for emotional well-being. Complete recovery typically takes 12-18 months, and some women may not return to pre-pregnancy hair density. Focus on overall hair health rather than immediate results.
The Role of Nutrition and Hair Vitamins After Pregnancy
Proper nutrition plays a vital role in supporting postpartum hair regrowth and overall hair health. Nutritional deficiencies common after pregnancy can contribute to prolonged hair loss and slow recovery.
Continue taking prenatal vitamins folic acid supplements even after delivery, especially if breastfeeding. These provide essential nutrients for hair growth, including iron, biotin, vitamin D, and B-complex vitamins. Folic acid specifically supports cellular division necessary for hair follicle function.
Postpartum vitamins should include adequate iron, as postpartum iron deficiency is common and directly linked to hair loss. Aim for 18-27mg daily unless blood tests indicate otherwise. Vitamin C enhances iron absorption when taken together.
A healthy hair diet emphasizes protein-rich foods, as hair is primarily composed of keratin protein. Include lean meats, fish, eggs, legumes, and nuts in daily meals. Aim for 25-30% of calories from high-quality protein sources.
| Nutrient | Daily Requirement | Food Sources | Hair Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iron | 18-27mg | Red meat, spinach, lentils | Prevents hair thinning |
| Biotin | 30-35mcg | Eggs, nuts, sweet potatoes | Strengthens hair shaft |
| Vitamin D | 600-800 IU | Fatty fish, fortified milk | Supports follicle health |
| Omega-3 | 1-2g | Salmon, walnuts, flaxseed | Reduces inflammation |
Effective Postpartum Hair Care Strategies
Implementing comprehensive postpartum hair care strategies helps minimize damage and supports natural regrowth processes. Focus on gentle handling, stress reduction, and protective measures during this vulnerable period.
Avoid heat and harsh chemicals that can further weaken already fragile hair. Air-dry hair when possible or use the lowest heat setting on styling tools. Chemical treatments like perms, relaxers, or permanent hair color should be postponed until hair regains strength.
Stress management is crucial, as chronic stress can prolong telogen effluvium and delay recovery. Practice relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. Adequate sleep supports hormone regulation and hair growth cycles.
Protective nighttime care prevents mechanical damage during sleep. Use silk or satin pillowcases to reduce friction, or wear a silk scarf or bonnet. Loose braids or top knots prevent tangling without creating tension.
Consider professional scalp treatments that promote circulation and provide deep nourishment. Monthly treatments with a licensed trichologist or experienced stylist can assess progress and adjust care routines as needed.
Regular trimming removes split ends and creates the appearance of thicker, healthier hair. Schedule trims every 6-8 weeks to maintain hair health during the regrowth phase.
FAQ :Postpartum Hair Loss Expert Tips and Coping Strategies
When does postpartum hair loss typically start?
Postpartum hair loss typically begins 1-6 months after delivery, with most women experiencing peak shedding around 3-4 months postpartum.
How long does postpartum hair loss last?
The shedding phase usually lasts 3-6 months, with complete regrowth taking 12-18 months as hormone levels stabilize and new growth cycles establish.
Are there any treatments for postpartum hair loss?
While no specific treatments stop the natural shedding process, gentle care routines, proper nutrition, and stress management support healthy regrowth.
What vitamins can help with postpartum hair loss?
Prenatal vitamins containing iron, biotin, folic acid, and vitamin D support hair health, along with omega-3 fatty acids and adequate protein intake.