Many new mothers experience significant hair shedding after giving birth, which can be both surprising and concerning. Postpartum hair loss affects up to 90% of women and is a completely normal part of the post-pregnancy recovery process. Understanding the causes behind this temporary condition and learning effective management strategies can help new mothers navigate this challenging phase with confidence.
This comprehensive guide explores the science behind hair loss after childbirth, hormonal triggers, timeline expectations, and proven management techniques to support healthy hair regrowth during the postpartum pe
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Postpartum Hair Loss
Postpartum hair loss is a temporary condition characterized by excessive hair shedding that typically occurs 2-4 months after delivery. This phenomenon, medically known as postpartum telogen effluvium, involves a sudden shift in the hair growth cycle that causes previously retained hairs to shed simultaneously.
During pregnancy, elevated hormone levels keep hair in the anagen (growth) phase longer than usual. This results in thicker, fuller hair that many women enjoy during their second and third trimesters. However, after delivery, hormone changes hair loss patterns dramatically as these protective hormones drop to pre-pregnancy levels.
The condition affects the entire scalp uniformly, unlike male pattern baldness or other localized hair loss causes. Women may notice increased hair in their brush, shower drain, or on their pillow. While alarming, this postpartum hair thinning is temporary and rarely leads to permanent baldness.
Key Characteristics of Postpartum Hair Loss
- Diffuse shedding across the entire scalp
- Increased daily hair fall of 100-300+ strands
- Temporary duration lasting 6-12 months
- No permanent damage to hair follicles
- Natural part of postpartum recovery
How Hormone Changes Trigger Hair Loss After Childbirth
Hormones and hair loss are intricately connected, with pregnancy creating dramatic fluctuations that directly impact hair retention and shedding patterns. Understanding these hormonal mechanisms helps explain why hair loss after childbirth occurs so predictably in new mothers.
During pregnancy, estrogen and progesterone levels increase dramatically, creating an environment that prolongs the hair growth phase. These elevated hormones essentially “pause” the normal shedding process, allowing women to retain hair that would typically fall out during the natural hair growth cycle.
After delivery, hormone levels plummet rapidly within 24-48 hours. This sudden drop triggers a synchronized shift of hair follicles from the anagen (growth) phase to the telogen (resting) phase. The result is massive hair shedding after pregnancy as months of retained hair are released simultaneously.
The Hair Growth Cycle and Pregnancy
| Phase | Normal Duration | During Pregnancy | Postpartum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anagen (Growth) | 2-7 years | Extended duration | Returns to normal |
| Catagen (Transition) | 2-3 weeks | Minimal activity | Increased activity |
| Telogen (Resting) | 2-3 months | Reduced numbers | Dramatically increased |
Hormonal Causes of Postpartum Hair Loss
Several specific hormones contribute to postpartum hair loss, with estrogen playing the most significant role in this temporary condition. Understanding these hormonal factors helps explain why some women experience more severe shedding than others.
Estrogen and hair loss have an inverse relationship – higher estrogen levels promote hair retention, while dropping levels trigger shedding. During pregnancy, estrogen levels can increase 100-fold, creating an artificial environment that keeps hair in the growth phase longer than normal.
Progesterone also plays a supporting role in maintaining hair during pregnancy. This hormone works synergistically with estrogen to create optimal conditions for hair retention and thickness. When progesterone levels drop postpartum, it compounds the shedding effect initiated by declining estrogen.
Thyroid hormones can also influence postpartum hair loss duration and severity. Postpartum thyroiditis affects 5-10% of new mothers and can exacerbate hair shedding. Additionally, prolactin elevation during breastfeeding may prolong the recovery period for some women.
Additional Hormonal Factors
- Androgens: Temporary increase as estrogen drops
- Cortisol: Elevated due to stress and sleep deprivation
- Iron deficiency: Common postpartum, affecting hair growth
- Nutritional deficits: Impact on hormone production and hair health
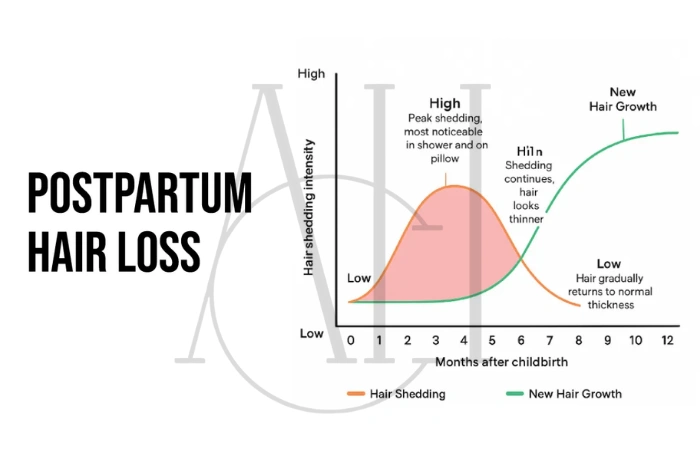
When Postpartum Hair Loss Starts and Stops
The timeline for postpartum hair loss follows a predictable pattern, though individual variations exist based on hormonal recovery, breastfeeding status, and overall health factors.
Most women notice initial signs of hair loss after childbirth beginning around 2-4 months postpartum. This delay occurs because hair follicles need time to transition from the growth phase to the shedding phase. The peak shedding period typically occurs between 4-6 months after delivery.
Postpartum hair loss duration generally ranges from 6-12 months total, with most women seeing significant improvement by their child’s first birthday. However, breastfeeding mothers may experience prolonged shedding due to continued hormonal influences from prolactin and suppressed ovulation.
Timeline Breakdown
Months 1-2: Minimal shedding as hormones begin adjusting Months 3-4: Initial increase in daily hair loss becomes noticeable Months 4-6: Peak shedding period with maximum daily hair fall Months 6-9: Gradual reduction in shedding as regrowth begins Months 9-12: Significant improvement with new hair growth visible
Recovery timelines can vary based on individual factors including age, nutrition, stress levels, and whether the mother is breastfeeding. Some women may notice complete resolution within 6 months, while others require up to 18 months for full hair density restoration.
How to Manage Postpartum Hair Loss
Effective postpartum hair loss treatment focuses on supporting the natural recovery process while minimizing additional stress on vulnerable hair follicles. While the condition cannot be completely prevented, several strategies can help manage symptoms and promote healthy regrowth.
Nutritional support forms the foundation of hair loss management. Key nutrients for hair health include iron, protein, biotin, zinc, and vitamins D and B12. Many postpartum women have depleted nutrient stores from pregnancy and breastfeeding, making supplementation important for optimal recovery.
Gentle hair handling techniques can minimize mechanical damage during the shedding phase. This includes using wide-toothed combs, avoiding tight hairstyles, and reducing heat styling frequency. Chemical treatments like coloring or perming should be postponed until shedding stabilizes.
Medical evaluation may be warranted if shedding continues beyond 12 months or if other symptoms suggest underlying conditions. Postpartum thyroiditis, iron deficiency anemia, or autoimmune conditions can complicate recovery and require specific treatment.
Management Strategies
Nutritional Support:
- Maintain adequate protein intake (50-75g daily)
- Continue prenatal vitamins or specialized hair supplements
- Ensure sufficient iron intake, especially if breastfeeding
- Stay hydrated and maintain balanced meals
Scalp Care:
- Use sulfate-free, gentle shampoos
- Massage scalp to promote circulation
- Consider essential oils like rosemary or peppermint
- Avoid overwashing (2-3 times weekly maximum)
- Practice relaxation techniques
- Prioritize sleep when possible
- Seek support from family and friends
- Consider professional counseling if needed
Tips for Hair Care During Postpartum Hair Loss
Implementing proper hair care after childbirth can significantly impact the comfort and appearance during the shedding phase while supporting healthy regrowth. These evidence-based strategies focus on minimizing damage while maintaining scalp health.
Choose styling techniques that create volume and fullness without damaging fragile hair. Layered cuts can help disguise thinning areas and make remaining hair appear fuller. Root-lifting products and volumizing mousses can provide temporary fullness without weighing hair down.
Protective styling becomes crucial during peak shedding months. Loose braids, gentle headbands, and silk or satin pillowcases can reduce friction and breakage. Avoid rubber bands, tight ponytails, and styles that pull on the hairline where postpartum hair thinning is often most noticeable.
Color and chemical processing should be approached cautiously during the shedding phase. If coloring is necessary, opt for temporary or semi-permanent options rather than permanent dyes with ammonia or bleach. Professional consultation can help determine the safest timing for any chemical treatments.
Daily Care Routine
Morning Routine:
- Use leave-in conditioner on damp hair
- Apply volumizing mousse to roots
- Style gently with wide-barrel brush
- Finish with lightweight holding spray
Weekly Treatments:
- Deep conditioning mask once weekly
- Scalp massage with nourishing oils
- Gentle exfoliation to remove buildup
- Protein treatments if recommended by professional
Protective Measures:
- Sleep on silk or satin pillowcase
- Use microfiber towel for drying
- Minimize heat styling frequency
- Wear protective styles during exercise
FAQ :Postpartum Hair Loss Causes and Management
When does postpartum hair loss typically begin and end?
Postpartum hair loss typically begins 2-4 months after delivery and resolves within 6-12 months as hormones stabilize and the natural hair growth cycle resumes.
What hormonal changes cause hair loss postpartum?
The dramatic drop in estrogen and progesterone levels after childbirth triggers hormonal hair loss after baby by shifting hair follicles from growth phase to shedding phase simultaneously.
How can you manage hair loss after childbirth?
Hair loss after childbirth can be managed through proper nutrition, gentle hair handling, stress reduction, and maintaining a healthy scalp care routine while avoiding harsh styling practices.
Do hair care tips help with postpartum hair loss?
Yes, proper hair care techniques including gentle styling, protective measures, and nourishing treatments can minimize breakage and support healthy regrowth during postpartum hair loss.