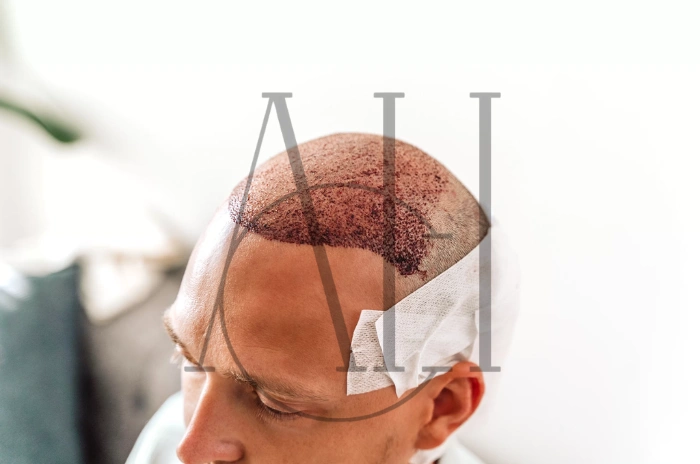
When considering a hair transplant, understanding the role of medications in your treatment journey is crucial for optimal results. Aspirin, one of the most commonly used medications worldwide, has gained attention not only for its traditional pain-relieving properties but also for its potential effects on hair health and transplant procedures. This comprehensive guide explores the relationship between aspirin and hair transplantation, helping you make informed decisions about your treatment. Many patients undergoing hair transplant in Turkey and other locations often wonder about continuing their regular medications, particularly antiplatelet drugs like aspirin. The interaction between aspirin and hair transplant procedures involves complex considerations regarding bleeding risks, healing processes, and post-operative care. Understanding these factors is essential for anyone planning to undergo this life-changing procedure.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Aspirin and its Alternative Use as a Hair Growth and Loss Treatment?
Aspirin, scientifically known as acetylsalicylic acid, belongs to a class of medications called nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Originally developed for pain relief and fever reduction, aspirin has found numerous applications beyond its traditional uses. In recent years, researchers and hair care enthusiasts have explored aspirin’s potential benefits for hair health and growth.
The compound works by inhibiting cyclooxygenase enzymes, which reduces inflammation and affects blood clotting mechanisms. These properties have led to investigations into aspirin for hair loss treatment, as inflammation and poor circulation are often contributing factors to hair thinning and loss. Some studies suggest that aspirin’s anti-inflammatory effects may help create a healthier scalp environment for hair growth.
When applied topically, aspirin can potentially address several scalp conditions that may contribute to hair loss. The medication’s ability to reduce inflammation, improve circulation, and provide gentle exfoliation has made it an interesting alternative treatment option. However, it’s important to note that while these properties are promising, aspirin should not be considered a primary treatment for serious hair loss conditions without proper medical consultation.
Key mechanisms of aspirin in hair care include:
- Cyclooxygenase enzyme inhibition leading to reduced inflammatory responses
- Salicylic acid content providing keratolytic and exfoliating properties
- Platelet aggregation inhibition potentially improving microcirculation
- pH modification creating an environment less favorable to certain scalp bacteria
Advantages of Using Aspirin for Hair Growth and Loss
Anti-inflammatory Properties
Aspirin’s primary advantage in hair care lies in its powerful anti-inflammatory properties. Scalp inflammation can significantly impede hair growth by creating an hostile environment for hair follicles. When inflammation occurs around hair follicles, it can disrupt the natural growth cycle and lead to premature hair loss. Aspirin helps reduce this inflammation, potentially allowing follicles to function more effectively.
The anti-inflammatory action of aspirin can be particularly beneficial for individuals with conditions like seborrheic dermatitis or scalp psoriasis. These conditions often contribute to hair loss through chronic inflammation, and aspirin’s therapeutic effects may help manage these symptoms. Regular use of aspirin-based treatments may help maintain a healthier scalp environment conducive to hair growth.
Benefits of anti-inflammatory action include:
- Reduction of cytokine production that damages hair follicles
- Decreased prostaglandin synthesis leading to less follicular inflammation
- Improved follicular blood supply through reduced vascular inflammation
- Enhanced nutrient delivery to hair roots through better circulation
Scalp Exfoliation
Another significant advantage of using aspirin for hair loss treatment is its exfoliating properties. The salicylic acid component in aspirin helps remove dead skin cells and excess sebum from the scalp surface. This exfoliation process can unclog hair follicles that may be blocked by buildup, allowing for better hair growth and improved scalp health.
Gentle exfoliation also enhances the absorption of other hair care products and treatments. When the scalp is free from excessive buildup, nutrients and active ingredients can penetrate more effectively to reach the hair follicles. This improved accessibility can enhance the overall effectiveness of your hair care routine and support better growth outcomes.
Exfoliation benefits include:
- Removal of follicle-blocking keratin plugs and dead skin cells
- Increased penetration of topical hair growth treatments
- Improved scalp hygiene and reduced bacterial overgrowth
- Enhanced natural sebum distribution along hair shafts
Improved Circulation
Aspirin’s blood-thinning properties can potentially improve circulation to the scalp, which is essential for healthy hair growth. Better blood flow means more nutrients and oxygen reach the hair follicles, supporting their metabolic functions and growth processes. Poor circulation is often linked to hair thinning and loss, making this benefit particularly valuable.
Enhanced circulation also helps remove waste products from the scalp area more efficiently. This improved waste removal, combined with better nutrient delivery, creates an optimal environment for hair follicle health. The increased blood flow may also help maintain the health of existing hair strands, reducing breakage and improving overall hair quality.
Circulation improvements include:
- Enhanced oxygen delivery to follicular dermal papilla cells
- Increased nutrient transport including vitamins and minerals
- Better waste product removal from follicular environment
- Improved temperature regulation of the scalp microenvironment
Antimicrobial Effects
Aspirin possesses mild antimicrobial properties that can help address bacterial and fungal infections on the scalp. These infections can contribute to hair loss by damaging follicles and creating inflammatory conditions. By helping to control microbial growth, aspirin may support scalp health and prevent infection-related hair loss.
The antimicrobial effects are particularly beneficial for individuals prone to scalp infections or those with compromised scalp barriers. Regular use of aspirin treatments may help maintain the scalp’s natural microbial balance, preventing the overgrowth of harmful organisms that could interfere with hair growth processes.
Antimicrobial benefits include:
- Inhibition of Malassezia species linked to dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis
- Reduction of Propionibacterium acnes in scalp follicles
- Prevention of secondary bacterial infections in damaged scalp areas
- Maintenance of healthy scalp pH that discourages pathogenic growth
Reduction in DHT
Some research suggests that aspirin may help reduce the effects of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone strongly linked to male pattern baldness. While the mechanism is not fully understood, the anti-inflammatory properties of aspirin may help mitigate some of the damaging effects of DHT on hair follicles. This potential benefit makes aspirin an interesting adjunct treatment for androgenetic alopecia.
The reduction in DHT-related inflammation could help preserve existing hair and potentially slow the progression of pattern hair loss. However, it’s important to note that aspirin alone is unlikely to completely counteract DHT effects, and more established treatments like finasteride or minoxidil remain the gold standard for DHT-related hair loss.
DHT-related benefits may include:
- Interference with DHT-induced inflammatory cascades
- Potential modulation of 5-alpha reductase activity
- Reduction of follicular miniaturization processes
- Protection against DHT-mediated follicular apoptosis
Accessible and Cost-Effective
One of the most practical advantages of using aspirin for hair care is its accessibility and affordability. Aspirin is readily available over-the-counter in most locations and costs significantly less than many specialized hair loss treatments. This accessibility makes it an attractive option for individuals seeking budget-friendly alternatives to expensive hair care products.
The cost-effectiveness of aspirin allows for consistent long-term use without significant financial burden. This affordability factor is particularly important since hair growth treatments typically require sustained use over several months to show meaningful results.
Cost and accessibility advantages:
- Available without prescription in most countries worldwide
- Significantly cheaper than commercial hair loss treatments
- Long shelf life allowing bulk purchasing for extended use
- No need for specialized medical consultations for basic use
Disadvantages of Using Aspirin for Hair Growth and Loss
Limited Scientific Evidence
Despite the theoretical benefits, there is limited high-quality scientific evidence supporting aspirin’s effectiveness for hair growth. Most claims are based on anecdotal reports or small-scale studies that may not provide reliable conclusions. The lack of comprehensive clinical trials makes it difficult to determine the true efficacy of aspirin for hair loss treatment.
Without robust scientific backing, patients may waste time and resources on treatments that may not provide significant benefits. It’s crucial to approach aspirin-based hair treatments with realistic expectations and consider them as complementary rather than primary treatment options. Consulting with healthcare professionals remains essential for evidence-based hair loss management.
Evidence limitations include:
- Absence of large-scale randomized controlled trials
- Lack of standardized dosing and application protocols
- Limited peer-reviewed research on topical aspirin for hair loss
- Most evidence being anecdotal or from small observational studies
Potential for Scalp Irritation
Aspirin can cause scalp irritation, particularly in individuals with sensitive skin or those using high concentrations. The acidic nature of aspirin may lead to redness, itching, burning sensations, or even chemical burns if used improperly. These adverse reactions can actually worsen hair loss by creating additional scalp trauma and inflammation.
People with existing scalp conditions or allergies to salicylates should exercise particular caution when considering aspirin treatments. Starting with lower concentrations and patch testing can help identify potential sensitivity issues before applying treatments to the entire scalp area.
Irritation risks include:
- Contact dermatitis from salicylate sensitivity
- Chemical burns from high concentrations or prolonged exposure
- Increased scalp sensitivity leading to chronic irritation
- Potential worsening of existing inflammatory scalp conditions
Aspirin is Not a Cure for Medical Hair Growth and Loss
It’s important to understand that aspirin is not a cure for medical conditions causing hair loss, such as androgenetic alopecia, alopecia areata, or thyroid disorders. While it may provide some supportive benefits, aspirin cannot address the underlying causes of these conditions. Relying solely on aspirin for serious hair loss conditions may delay appropriate medical treatment.
Patients with significant hair loss should seek proper medical evaluation to identify underlying causes and receive appropriate treatment. Aspirin may be used as a complementary treatment alongside established therapies, but it should not replace proven medical interventions when indicated.
Medical limitations include:
- Cannot address genetic predisposition to androgenetic alopecia
- Ineffective against autoimmune causes of hair loss
- No ability to correct hormonal imbalances causing hair loss
- Cannot replace FDA-approved treatments for pattern hair loss
Not Suitable for Everyone
Certain individuals should avoid using aspirin for hair care, including those with aspirin allergies, bleeding disorders, or those taking blood-thinning medications. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should also exercise caution with topical aspirin use. These contraindications highlight the importance of medical consultation before starting any aspirin-based hair treatment regimen.
People scheduled for surgical procedures, including hair transplant surgery, need to be particularly careful about aspirin use due to its blood-thinning effects. The timing of discontinuation becomes crucial to prevent bleeding complications during and after the procedure.
Contraindications include:
- Known allergies to aspirin or salicylates
- Active bleeding disorders or anticoagulant therapy
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding periods
- Scheduled surgical procedures including hair transplant

How Can Aspirin Be Turned into a Hair Care Product for Hair Growth?
Converting aspirin into effective hair care products requires careful preparation and consideration of concentration levels. The most common method involves crushing uncoated aspirin tablets and mixing them with suitable carriers like shampoos, oils, or water-based solutions. The typical ratio ranges from 2-4 aspirin tablets per application, depending on the intended use and individual tolerance.
When preparing aspirin treatments, it’s essential to ensure complete dissolution to prevent granular particles that could cause physical irritation to the scalp. Mixing aspirin with warm water or gentle heat can facilitate dissolution, but excessive heat should be avoided as it may degrade the active compounds. Adding ingredients like honey or aloe vera can help buffer the acidic nature of aspirin and provide additional soothing properties.
The pH level of aspirin solutions should be monitored and adjusted if necessary to prevent excessive acidity that could damage the scalp or hair. Most effective formulations maintain a pH between 4.5 and 6.5, which is slightly acidic but within the range that hair and scalp can tolerate comfortably.
Preparation guidelines include:
- Use only uncoated aspirin tablets to avoid inactive ingredients
- Crush tablets thoroughly to ensure complete dissolution
- Start with lower concentrations and gradually increase as tolerated
- Test pH levels and adjust with buffering agents if necessary
- Prepare fresh solutions for each use to maintain potency
- Store any unused portions in refrigerator for maximum 24 hours
Do You Need Medications after a Hair Transplant?
Post-operative medication protocols are essential components of successful hair transplant procedures. Most surgeons prescribe a combination of medications to prevent infection, reduce inflammation, minimize pain, and optimize healing conditions. These medications typically include antibiotics to prevent bacterial infections at the transplant sites, which could compromise graft survival and overall results.
Anti-inflammatory medications, usually prescribed corticosteroids, help reduce swelling and inflammation around the transplanted area. This reduction in inflammation is crucial for graft survival and patient comfort during the initial healing phase. Pain management medications ensure patient comfort during the recovery period, allowing for better rest and reduced stress, which supports healing.
Some surgeons also prescribe medications to promote hair growth, such as minoxidil, which may be started several weeks after the procedure. These growth-promoting medications can enhance the overall results of the transplant by supporting both transplanted and existing hair. The specific medication regimen varies depending on the surgical technique used, patient health status, and surgeon preferences.
Standard post-hair transplant medications include:
- Oral antibiotics for 5-7 days to prevent infection
- Topical antibiotic ointments for donor and recipient areas
- Anti-inflammatory medications to reduce swelling
- Pain medications for comfort during initial recovery
- Specialized shampoos for gentle cleansing
- Growth-promoting treatments like minoxidil after initial healing
| Medication Type | Purpose | Duration | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotics | Infection prevention | 5-7 days | Amoxicillin, Cephalexin |
| Anti-inflammatory | Swelling reduction | 3-5 days | Prednisolone, Ibuprofen |
| Pain relievers | Comfort management | As needed | Acetaminophen, Tramadol |
| Growth promoters | Enhanced results | Long-term | Minoxidil, Finasteride |
What is the relationship between hair transplant surgery and current oral medication?
Understanding the relationship between hair transplant surgery and existing medications is crucial for patient safety and optimal outcomes. Many commonly prescribed medications can significantly impact surgical procedures, affecting bleeding risks, healing processes, and anesthetic interactions. Patients must provide complete medication histories to their surgical teams to ensure proper pre-operative planning.
Medication interactions can affect multiple aspects of the surgical process, from anesthesia administration to post-operative healing. Some medications increase bleeding risks, while others may interfere with wound healing or immune responses. The timing of medication adjustments must be carefully planned to balance surgical safety with the management of underlying medical conditions.
Pre-operative medication review should include:
- Complete list of prescription medications with dosages
- Over-the-counter medications and supplements
- Herbal remedies and alternative treatments
- Previous adverse reactions to medications
- Underlying medical conditions requiring ongoing treatment
- Consultation with prescribing physicians for medication adjustments
Anticoagulants (blood-thinning drugs)
Anticoagulant medications like warfarin, heparin, and newer agents like rivaroxaban significantly increase bleeding risks during hair transplant procedures. These medications prevent blood clot formation, which is essential for normal hemostasis during surgery. Excessive bleeding can compromise graft survival and increase the risk of post-operative complications.
Most surgeons require patients to discontinue anticoagulants several days before surgery, with the exact timing depending on the specific medication and the patient’s underlying medical conditions. This discontinuation must be carefully coordinated with the prescribing physician to balance surgical safety with the risk of thromboembolic events. Bridge therapy with shorter-acting agents may be necessary for high-risk patients.
Anticoagulant considerations include:
- Warfarin requires 5-7 days discontinuation with INR monitoring
- Direct oral anticoagulants need 2-3 days cessation depending on kidney function
- Heparin products require 12-24 hours discontinuation
- Bridge therapy may be necessary for high-risk cardiovascular patients
Anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin, can interfere with platelet function and increase bleeding risks. These medications also affect the inflammatory response, which is a normal part of the healing process. While inflammation needs to be controlled, completely suppressing it may impair healing and graft integration.
The timing of NSAID discontinuation varies, but most surgeons recommend stopping these medications 7-10 days before surgery. Alternative pain management strategies may be necessary during this period, and patients should work with their healthcare providers to develop appropriate substitution plans.
NSAID management includes:
- Discontinuation 7-10 days before surgery for most agents
- Longer discontinuation periods for long-acting NSAIDs
- Alternative pain management with acetaminophen
- Gradual reintroduction after initial healing phase
Antiplatelet drugs
Antiplatelet drugs like clopidogrel, ticagrelor, and aspirin specifically target platelet aggregation, which is essential for blood clotting. These medications are commonly prescribed for cardiovascular protection but pose significant bleeding risks during surgical procedures. The effects of these medications can persist for several days to weeks after discontinuation.
Patients taking antiplatelet drugs require careful pre-operative planning, including coordination with cardiologists or other specialists who originally prescribed these medications. The timing of discontinuation must balance surgical safety with cardiovascular risks, and some patients may require specialized monitoring during the discontinuation period.
Antiplatelet drugs management includes:
- Aspirin cessation 10-14 days before surgery
- Clopidogrel discontinuation 7-10 days pre-operatively
- Coordination with cardiologist for high-risk patients
- Possible platelet function testing before surgery
Steroids
Corticosteroid medications can impair wound healing and increase infection risks, which are particular concerns for hair transplant procedures. These medications suppress the immune system and interfere with the inflammatory cascade necessary for proper healing. Long-term steroid use can also affect skin integrity and graft survival rates.
Patients on chronic steroid therapy may require dose adjustments or temporary discontinuation before surgery, depending on the underlying condition being treated. The decision to modify steroid therapy must involve the prescribing physician, as abrupt discontinuation can cause serious complications in some patients.
Steroid considerations include:
- Gradual tapering rather than abrupt discontinuation
- Stress dose steroids may be needed during surgery
- Increased infection monitoring post-operatively
- Delayed wound healing expectations
Vitamins and supplements
Many vitamins and supplements can affect surgical outcomes, with some increasing bleeding risks while others may actually support healing processes. Vitamin E, fish oil supplements, and certain herbal products can increase bleeding tendencies. Conversely, vitamins C and D, along with zinc, may support healing when used appropriately.
A comprehensive review of all supplements is necessary before hair transplant surgery, as many patients don’t consider these over-the-counter products as “real medications.” Some supplements may need to be discontinued weeks before surgery, while others might be continued or even added to support optimal healing.
Supplement management includes:
- Vitamin E discontinuation 2 weeks before surgery
- Fish oil cessation 1-2 weeks pre-operatively
- Continuation of vitamin C and D for healing support
- Herbal supplement review for bleeding risks
Blood Pressure Lowering Drugs
Antihypertensive medications generally don’t need to be discontinued before hair transplant surgery, but they may require monitoring and possible adjustment during the peri-operative period. Some blood pressure medications can interact with anesthetic agents or affect the body’s response to surgical stress. Beta-blockers, in particular, may mask some physiological responses to complications.
Blood pressure control is actually beneficial for surgical outcomes, as uncontrolled hypertension can increase bleeding risks and compromise healing. Patients should continue their prescribed antihypertensive regimens unless specifically instructed otherwise by their surgical team.
Blood pressure medication considerations:
- Continue most antihypertensives through surgery
- Monitor for interactions with anesthetic agents
- Adjust dosing if significant blood pressure changes occur
- Special attention to beta-blockers and their effects
Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications
Psychiatric medications generally don’t require discontinuation before hair transplant surgery, but they may interact with anesthetic agents and pain medications. Some antidepressants can affect bleeding risks, while others may influence pain perception and healing processes. Benzodiazepines used for anxiety may interact with sedation protocols.
Maintaining psychological stability during the surgical period is important for overall outcomes, so psychiatric medications are usually continued with appropriate monitoring. The anesthesia team should be informed about all psychiatric medications to ensure safe drug interactions and appropriate sedation protocols.
Psychiatric medication management includes:
- Continuation of most antidepressants and anxiolytics
- Special attention to SSRI bleeding effects
- Coordination with anesthesia team for drug interactions
- Monitoring for mood changes during recovery period
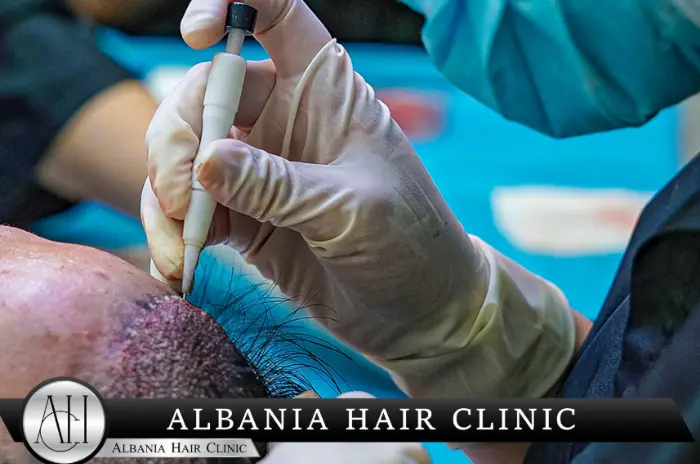
Can I take Aspirin Before My Hair Transplant?
Taking aspirin before a hair transplant procedure is generally not recommended due to its significant effects on blood clotting mechanisms. Aspirin irreversibly inhibits platelet function, which can lead to excessive bleeding during and after the surgical procedure. This increased bleeding risk can compromise graft survival and create additional complications during the recovery period.
The decision to discontinue aspirin must be individualized based on the patient’s medical history and the reason for aspirin therapy. Patients taking aspirin for cardiovascular protection may require careful evaluation by their cardiologist before discontinuation. The risk-benefit analysis must consider both the surgical risks of continued aspirin use and the cardiovascular risks of temporary discontinuation.
Pre-operative aspirin considerations include:
- Assessment of cardiovascular risk without aspirin
- Coordination with cardiologist for high-risk patients
- Discussion of alternative antiplatelet strategies if needed
- Clear understanding of avoid aspirin before surgery protocols
Aspirin – stop 10 days before surgery
The standard recommendation is to avoid aspirin before surgery for at least 10 days prior to the hair transplant procedure. This timeframe allows for the regeneration of new platelets with normal function, as aspirin’s effects on existing platelets are irreversible. The 10-day period ensures that the majority of affected platelets have been replaced by normally functioning ones.
Some surgeons may recommend a longer discontinuation period, particularly for patients taking high-dose aspirin or those with additional bleeding risk factors. The exact timing should always be confirmed with the surgical team, as individual patient factors may warrant modified recommendations. During this period, patients should avoid all aspirin-containing products, including some over-the-counter pain relievers and combination medications.
Alternative pain management strategies may be necessary during the aspirin-free period, particularly for patients who rely on it for chronic pain control. Acetaminophen is generally considered safe and can be used for mild to moderate pain relief without affecting platelet function.
Aspirin discontinuation protocol:
- Stop all aspirin-containing medications 10 days before surgery
- Check labels of combination medications for hidden aspirin
- Use acetaminophen for pain relief during aspirin-free period
- Confirm discontinuation timing with surgical team
How to Use Aspirin for Hair Growth
Aspirin Shampoo Treatment
Creating an aspirin-enhanced shampoo involves crushing 2-3 uncoated aspirin tablets and mixing them with your regular shampoo. The mixture should be prepared fresh for each use to maintain potency and prevent degradation of the active ingredients. Dissolve the crushed aspirin in a small amount of warm water before adding it to the shampoo to ensure even distribution.
Apply the aspirin-enhanced shampoo to wet hair, focusing on the scalp area rather than the hair lengths. Gently massage the scalp for 2-3 minutes to allow the aspirin to work on the scalp surface, then leave it on for an additional 3-5 minutes before rinsing thoroughly. This treatment can be used 1-2 times per week, depending on scalp sensitivity and tolerance.
Monitor for any signs of irritation, such as redness, itching, or burning sensations, and discontinue use if these symptoms occur. Start with lower concentrations and less frequent applications to assess tolerance before increasing intensity.
Aspirin shampoo preparation steps:
- Crush 2-3 uncoated aspirin tablets into fine powder
- Dissolve powder in 1-2 tablespoons warm water
- Mix dissolved aspirin with regular shampoo portion
- Apply immediately to avoid degradation of active ingredients
- Focus application on scalp rather than hair lengths
- Rinse thoroughly after 3-5 minutes contact time
Aspirin Hair Mask
An aspirin hair mask provides more intensive treatment by allowing longer contact time with the scalp. Crush 4-6 aspirin tablets and mix with 3-4 tablespoons of warm water to create a paste-like consistency. Adding a tablespoon of honey or aloe vera gel can help buffer the acidity and provide additional soothing properties.
Apply the mask to clean, damp hair, focusing primarily on the scalp and roots. Use gentle circular motions to work the mask into the scalp, then cover with a shower cap or plastic wrap. Leave the mask on for 15-20 minutes to allow maximum penetration and effect, then rinse thoroughly with lukewarm water followed by a gentle shampoo.
This intensive treatment should be used no more than once per week, as more frequent application may cause irritation or over-exfoliation of the scalp. Always perform a patch test before using a new aspirin mask formulation to check for sensitivity reactions.
Aspirin mask application process:
- Crush 4-6 aspirin tablets into fine powder
- Add warm water gradually to create paste consistency
- Include buffering agents like honey or aloe vera
- Apply to clean, damp scalp with gentle massage
- Cover with shower cap for enhanced penetration
- Leave for 15-20 minutes maximum exposure time
Aspirin Scalp Treatment
A targeted aspirin scalp treatment focuses on specific areas of concern or thinning. Dissolve 2 aspirin tablets in 2 tablespoons of warm water, then add a few drops of carrier oil like jojoba or coconut oil to create a more spreadable consistency. This combination provides the benefits of aspirin while the oil helps protect and moisturize the scalp.
Apply the treatment directly to problem areas using a cotton ball or your fingertips, gently massaging in circular motions. Focus on areas with thinning hair or scalp irritation, ensuring even coverage without oversaturating any area. Leave the treatment on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing with lukewarm water.
This targeted approach allows for precise application and may be better tolerated than full-scalp treatments. It can be used 2-3 times per week on specific areas while monitoring for any adverse reactions or improvements in scalp condition.
Targeted treatment application:
- Dissolve 2 aspirin tablets in warm water
- Add carrier oil for improved spreadability and protection
- Apply with cotton ball or fingertips to specific areas
- Use gentle circular massage motions
- Focus on thinning or problematic scalp areas
- Monitor for improvements or adverse reactions
| Aspirin Hair Treatment Method | Concentration | Frequency | Contact Time | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aspirin Shampoo | 2-3 tablets per application | 1-2 times per week | 3-5 minutes | General scalp health |
| Aspirin Hair Mask | 4-6 tablets per application | Once per week | 15-20 minutes | Intensive treatment |
| Aspirin Scalp Treatment | 2 tablets per application | 2-3 times per week | 10-15 minutes | Targeted problem areas |
Does Aspirin Really Promote Hair Growth?
The scientific evidence supporting aspirin’s ability to promote hair growth remains limited and largely theoretical. While aspirin possesses several properties that could theoretically benefit hair health, including anti-inflammatory effects and improved circulation, comprehensive clinical studies demonstrating significant hair growth benefits are lacking. Most claims are based on anecdotal reports and small-scale observations rather than rigorous scientific research.
The anti-inflammatory properties of aspirin may help create a healthier scalp environment, which could indirectly support hair growth. However, inflammation is just one of many factors that can contribute to hair loss, and addressing it alone may not be sufficient to promote significant new growth. Other factors such as genetics, hormones, nutrition, and overall health play more substantial roles in determining hair growth patterns.
While some individuals report positive results from using aspirin for hair loss, these improvements may be due to other factors such as improved scalp hygiene, massage effects from application, or psychological benefits. The placebo effect can be particularly strong in cosmetic treatments, making it difficult to determine the true efficacy of aspirin without controlled studies.
Current evidence limitations:
- Lack of randomized controlled trials specifically for hair growth
- Most evidence is anecdotal or from small observational studies
- Difficult to separate aspirin effects from other treatment variables
- Need for longer-term studies to assess sustained benefits
- Absence of standardized protocols for aspirin hair treatments
- Limited understanding of optimal concentrations and application methods
FAQ for Aspirin Role and Effects On Your Hair Transplant
What are the benefits of using aspirin for hair growth?
Aspirin may provide anti-inflammatory effects, improve scalp circulation, offer gentle exfoliation, and potentially reduce DHT-related damage, though scientific evidence supporting these benefits for hair growth remains limited.
Can aspirin cause side effects when used for hair growth?
es, aspirin can cause scalp irritation, redness, burning sensations, and allergic reactions, particularly in individuals with sensitive skin or aspirin allergies.
Is it safe to take aspirin before a hair transplant surgery?
No, it’s not safe to take aspirin before hair transplant surgery as it increases bleeding risks; aspirin should be discontinued at least 10 days before the procedure.
How does aspirin interact with hair transplant medications like minoxidil?
There are no known significant interactions between topical aspirin treatments and minoxidil, but both should be used under medical supervision to monitor for adverse effects.
What medications are typically prescribed after a hair transplant?
Post-hair transplant medications typically include antibiotics for infection prevention, anti-inflammatory drugs for swelling reduction, pain relievers, and sometimes growth-promoting treatments like minoxidil.
Can aspirin be used topically for hair care?
Yes, aspirin can be used topically in shampoos, masks, or scalp treatments, but it should be used carefully to avoid irritation and allergic reactions.
Are there any risks associated with using aspirin for hair growth?
Yes, risks include scalp irritation, allergic reactions, chemical burns from high concentrations, and potential interference with other medications or medical conditions.
Should aspirin be avoided after a hair transplant surgery?
Yes, antiplatelet drugs like aspirin should generally be avoided immediately after hair transplant surgery to prevent excessive bleeding and complications during the healing process.