Hair loss affects millions worldwide, and one of the primary culprits is a hormone known as DHT (dihydrotestosterone). Whether you’re dealing with male pattern baldness, thinning edges, or general hair shedding, understanding how DHT blockers work could be the first step toward hair restoration. This article breaks down the science, types, and effectiveness of these treatments, helping you make informed decisions about your hair loss treatment.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is DHT?
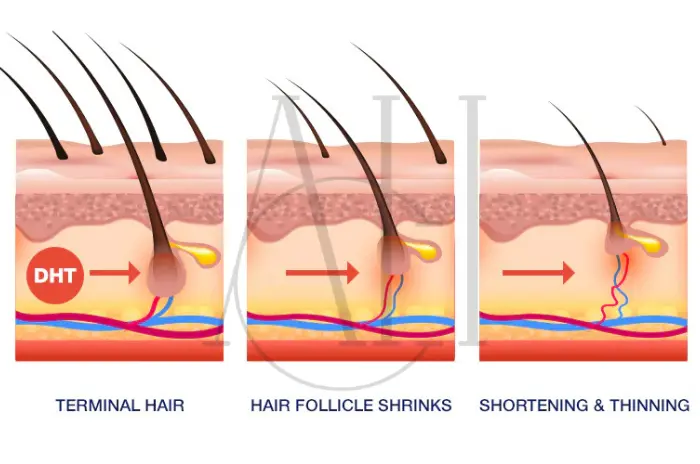
DHT is a hormone derived from testosterone through the action of an enzyme called 5-alpha reductase. While DHT plays important roles in male development and sexual function, it also has a destructive effect on hair follicles in genetically susceptible individuals.
When DHT binds to receptors in hair follicles, it causes a process called miniaturization. This gradually shrinks the follicles, making them produce progressively thinner and shorter hairs. Over time, the affected follicles become so small that they can no longer produce visible hair, leading to baldness.
The pattern of hair loss caused by DHT is predictable. In men, it typically begins with a receding hairline and crown thinning, eventually progressing to complete baldness on the top of the head. Women usually experience diffuse thinning across the crown while maintaining their hairline.
What is a DHT Blocker?
A DHT blocker is any substance—natural or synthetic—that inhibits the production or effects of DHT. These blockers aim to protect the hair follicles from damage, ultimately supporting hair growth and slowing down hair loss.
DHT Blockers
Prescription Medicine as DHT Blockers
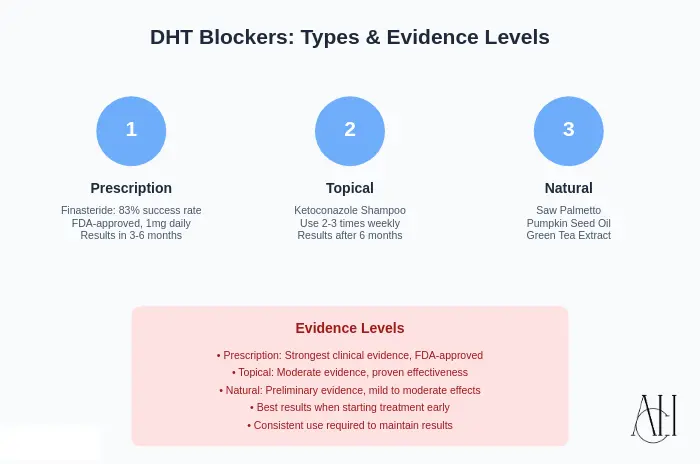
Prescription DHT blockers like Finasteride and Dutasteride are among the most effective options. They work by inhibiting the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme, which converts testosterone to DHT.
Shampoos and Conditioners as DHT Blockers
DHT blocking shampoos often contain ingredients like ketoconazole, saw palmetto, or caffeine. These shampoos cleanse the scalp while potentially reducing DHT at the follicular level.
Natural DHT Blockers (Foods and Vitamins)
Natural options include green tea, pumpkin seed oil, biotin, and zinc-rich foods. These may not be as powerful as medications but are generally safe and easy to incorporate into your routine.
Understanding DHT and Hair Loss
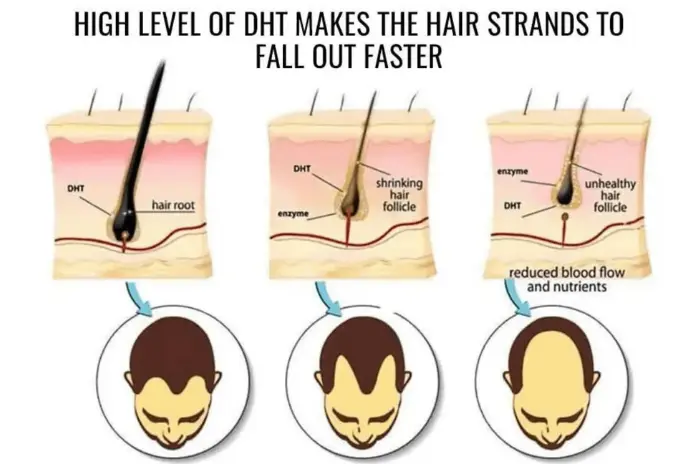
The link between DHT and hair loss is well-documented. DHT binds to receptors in scalp follicles, causing them to shrink. Over time, this results in male pattern baldness or female thinning patterns.
How DHT Causes Hair Loss
When DHT binds to hair follicle receptors, it leads to miniaturization. This means hair grows back thinner and weaker until it stops growing entirely. This is especially evident in individuals with a genetic predisposition to hair thinning.
What is DHT and its Effect on the Body?
Beyond hair, DHT impacts muscle mass, libido, and prostate health. While it’s essential for development, high levels of DHT in adults, particularly men, are linked to hair loss, acne, and prostate issues.
How Do DHT Blockers Work?
DHT blockers function by preventing the formation or binding of DHT to follicular receptors. This helps in maintaining hair density and promoting hair loss prevention. The result is healthier follicles and reduced hair shedding.
How Effective are DHT Blocking Medications?
Mid-Article Comparison Table: Natural vs. Prescription DHT Blockers
| Category | Examples | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Prescription | Finasteride, Dutasteride | Moderate to advanced hair loss. Requires consistent long-term use for visible results. Side effects may include decreased libido or hormonal imbalances. |
| Topical | Ketoconazole Shampoo, Topical Finasteride | Mild to moderate hair loss. Often used alongside oral treatments for enhanced results. May be safer for those concerned about systemic side effects. |
| Natural | Green Tea, Saw Palmetto, Pumpkin Seed Oil | Early-stage or preventive hair care. Preferred by those seeking holistic approaches. Effects may be slower and milder compared to medications. |
Finasteride and Dutasteride can reduce DHT levels by up to 70-90%. Many users experience visible hair restoration within 3 to 6 months. However, effectiveness varies based on age, stage of hair loss, and overall health.
The Most Effective Medical DHT Blocker Treatments
Medical DHT blocker treatments represent the gold standard for combating androgenetic alopecia. These FDA-approved medications have extensive clinical research supporting their effectiveness in stopping hair loss and promoting regrowth.
| Treatment | Type | DHT Reduction | Success Rate | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Finasteride | Oral | 70% | 90% stop loss, 65% regrowth | Low (2-5%) |
| Dutasteride | Oral | 95% | Higher than finasteride | Similar to finasteride |
| Minoxidil | Topical | Minimal | 60-70% improvement | Scalp irritation |
| Ketoconazole | Topical | Moderate | 30-40% improvement | Mild scalp dryness |
| Saw Palmetto | Oral/Topical | 20-30% | 25-35% improvement | Very low |
What are the Best Natural Remedies for Hair Growth?
Coconut Oil
Contains lauric acid and medium-chain fatty acids that penetrate the scalp and support overall hair health. It helps reduce protein loss in hair shafts and provides antimicrobial protection to the scalp.
Rosemary Oil
Enhances blood circulation in the scalp, stimulating hair follicles and potentially encouraging new growth. Some studies suggest it may perform comparably to Minoxidil with consistent use.
Olive Oil
Rich in antioxidants and vitamin E, olive oil helps nourish the scalp and moisturize hair. It also has anti-inflammatory properties that protect the hair follicle from oxidative stress.
Pumpkin Seed Oil
Shown in studies to block DHT production and promote thicker hair over time. It’s a popular supplement for individuals seeking natural hair regrowth strategies.
Sunflower Oil
Contains high levels of vitamin E and oleic acid, which reduce scalp inflammation and support healthy follicle function. It also helps retain moisture in the hair shaft.
Green Tea
Loaded with catechins, which inhibit DHT production and improve scalp circulation. Regular consumption or topical use may reduce shedding and enhance hair strength.
Jojoba Oil
Mimics natural scalp sebum, helping to moisturize and protect hair follicles. It’s especially useful for individuals with dry or sensitive scalps.
Types of DHT Blockers: A Scientific Evidence Review
Prescription DHT Blockers
Finasteride (Propecia)
Effective in reducing serum DHT levels and clinically proven to slow or halt hair loss. Long-term use is associated with sustained results, though potential side effects must be monitored.
Dutasteride
More potent than Finasteride, blocking both type I and II enzymes, leading to greater DHT suppression. Studies show higher regrowth rates, especially in individuals with advanced hair loss.
Topical DHT Blockers
Ketoconazole Shampoo
Originally developed as an anti-fungal, it also blocks DHT and reduces scalp inflammation. Often used 2–3 times per week to manage dandruff and thinning.
Topical Finasteride
Offers localized DHT suppression with fewer systemic risks than oral forms. Commonly used in combination with Minoxidil for synergistic results.
Natural DHT Blockers
Saw Palmetto
Derived from the serenoa repens plant, it inhibits 5-alpha-reductase, limiting DHT formation. Often found in supplement blends for hair loss.
Pumpkin Seed Oil
Has both anti-inflammatory and DHT-inhibiting properties. It may take 3–6 months of regular use to see visible benefits.
Green Tea
Rich in polyphenols and EGCG, green tea reduces DHT production and improves overall scalp health. Drinking it regularly or applying extracts can offer long-term benefits.
DHT Blockers Effectiveness and Realistic Results to Expect
Timeline for Results
Most users begin seeing improvements in 3–6 months. Full results typically take 12 months. However, some users may see earlier signs of reduced shedding and hair thickening within just 2 months. The timeline depends on the stage of hair loss and the type of treatment. Continued application or intake is necessary to maintain progress.
What Influences Success
Success depends on age, duration of hair loss, and genetics. Starting early increases the likelihood of regrowth. Hormonal health, stress levels, and scalp hygiene also play crucial roles. Those with early intervention often see better outcomes. Consistency and realistic expectations are key to long-term satisfaction.
Side Effects and Considerations
Prescription DHT Blockers
Possible side effects include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and mood changes. These effects are typically dose-dependent and may lessen over time. Regular medical checkups can help track hormonal fluctuations and detect complications early.
Topical Treatments
Generally have fewer side effects but may cause local irritation. Some users report redness, burning, or dryness on the scalp. Patch testing before full use can minimize allergic reactions. Topical forms like ketoconazole or topical finasteride are preferred by those sensitive to oral medications.
What to Watch For
Monitor for allergic reactions, hormonal imbalances, and unusual shedding. Sudden hair loss after starting a DHT blocker may signal telogen effluvium, which is temporary. Swelling, breast tenderness, or emotional shifts should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Do DHT Blockers Have Side Effects?
DHT Blockers and Skin Rashes
Some users report itching, flaking, or redness on the scalp. This may occur due to sensitivity to active ingredients or alcohol-based solutions. Switching to a gentler formula or moisturizing the scalp may help. In rare cases, rashes may spread beyond the scalp.
DHT Blockers and Sexual Issues
Reduced libido and erectile dysfunction are potential side effects. These usually result from hormonal changes due to lowered DHT. Most symptoms subside after discontinuing the medication.
DHT Blockers and Male Breast Tissue
Rare cases of gynecomastia (enlarged male breast tissue) have been reported. This happens due to hormonal shifts affecting estrogen and testosterone levels. It’s usually mild and reversible.
DHT Blockers and Testicular Disorder
There are rare reports of testicular pain or shrinkage. While uncommon, it’s crucial to monitor any unusual symptoms. These effects may result from long-term use or pre-existing conditions. Prompt medical attention ensures safety.
DHT Blockers and Liver Enzymes
Prescription medications may affect liver enzymes; regular monitoring is advised. Blood tests every 6–12 months can help track any changes. Those with liver conditions should proceed with caution.
DHT vs. testosterone
While both are androgens, DHT is a more potent derivative of testosterone. High DHT is strongly linked to hair loss, especially on the crown and hairline. Testosterone is vital for muscle growth, bone density, and sexual function. Blocking DHT does not significantly reduce testosterone.
DHT’s connection to balding
Male pattern baldness is driven by DHT’s action on genetically sensitive hair follicles. DHT shortens the growth phase of hair, leading to thinning. Over time, follicles shrink and eventually stop producing hair. Blocking DHT can slow or reverse this process.
How to Choose the Right DHT Blocker
Early-Stage Hair Loss
Start with natural options or topical solutions to reduce risks. These include saw palmetto, ketoconazole shampoo, and green tea. They’re ideal for people who prefer milder, holistic approaches.
Established Hair Loss
Prescription DHT blockers like Finasteride or Dutasteride may be necessary. These options provide stronger DHT suppression and are backed by clinical trials. They’re suitable for men with moderate to severe thinning.
Natural Preference
Look into natural DHT blockers like green tea, pumpkin seed oil, and saw palmetto. These are popular among those avoiding pharmaceutical interventions. Although results are subtler, they support scalp health and reduce inflammation.
Top Prescription DHT Blockers: Finasteride and Dutasteride
Both are highly effective, with Dutasteride having a broader impact. Finasteride blocks one type of enzyme, while Dutasteride blocks two. This makes Dutasteride more potent but possibly with more side effects.
How Long Does It Take DHT Blockers To Work?
Visible changes may appear in 3 to 6 months, with continued improvement over a year. Some users report initial shedding before regrowth begins. Full results are usually noticeable after 12 months of consistent use. Patience is key. Taking photos monthly helps track subtle improvements.
Alternatives to DHT Blockers for Hair Loss Treatment
-
Minoxidil (topical)
-
Hair transplant surgery
-
Microneedling
Who Cannot Use DHT Blockers?
-
Pregnant or breastfeeding women
-
Individuals with liver conditions
-
Those allergic to ingredients in the medication
What Does the DHT Hormone Do?
It plays a role in male development, such as prostate growth and hair patterning, but excessive DHT contributes to hair loss. It helps form secondary sex characteristics during puberty. However, it has adverse effects on hair follicles over time.
Why you Should Get Hair Transplant Instead of DHT Blockers?
For advanced hair loss, a hair transplant offers immediate and permanent results, while blockers work slowly and may not regrow hair. Transplants replace dead follicles with active ones. They’re ideal when medications no longer help.
What Happen When DHT Hormone Levels are High?
High DHT levels lead to hair follicle miniaturization, oily skin, and in some cases, prostate enlargement. Other signs include acne flare-ups and aggressive hair thinning. It may also contribute to mood swings. Managing DHT early can delay or prevent severe balding. Hormone testing helps identify abnormalities.
Things to Do to Balance the DHT Hormone
-
Eat a DHT-friendly diet (rich in zinc and omega-3)
-
Reduce stress
-
Use natural blockers like green tea
Why DHT Causes Hair Loss?
Because it shortens the hair growth cycle and shrinks the follicle, ultimately stopping hair production altogether. It binds to receptors in genetically sensitive follicles. The result is thinner, weaker strands over time. DHT resistance varies between individuals. Blocking it preserves and strengthens hair density.
Usage of DHT Blocker for Hair Loss
DHT blockers should be used consistently and under medical supervision for optimal hair loss treatment outcomes. Skipping doses reduces effectiveness and can cause shedding. Combining treatments enhances results. Periodic evaluations ensure long-term safety and success. Always follow dosage instructions carefully.
Using Topical DHT Blockers like Shampoos and Serums
Topical DHT blocker products offer a convenient way to target hair loss directly at the scalp level. These formulations can complement oral medications or serve as standalone treatments for those who prefer to avoid systemic medications.
DHT blocker shampoos typically contain ingredients like ketoconazole, saw palmetto, or biotin for hair health. Ketoconazole, an antifungal medication, has been shown to have anti-androgenic properties that can help reduce DHT levels at the scalp.
Topical serums often combine multiple natural DHT blockers in concentrated formulations. These may include saw palmetto extract, pumpkin seeds oil, green tea polyphenols, and various vitamins that support hair health.
The advantage of topical DHT blocker treatments is their targeted action and reduced risk of systemic side effects. However, they generally provide more modest results compared to oral medications.
Who Is a Good Candidate for DHT Blocker Treatment
Determining candidacy for DHT blocker treatment involves evaluating several factors, including the type of hair loss, its progression stage, age, and overall health status.
Ideal candidates are those with androgenetic alopecia who still have active hair follicles. This is typically indicated by the presence of fine, miniaturized hairs in affected areas rather than completely smooth scalp.
Men experiencing early to moderate hair loss respond best to DHT blocker treatments. Those with extensive baldness may still benefit from treatment to preserve remaining hair.
Understanding the Role of DHT in Female Hair Loss
Female hair loss patterns differ significantly from male baldness, with DHT playing a more complex role in women’s hair health. Women typically experience diffuse thinning across the crown area rather than distinct receding patterns.
DHT and female hair loss involves interactions with estrogen, progesterone, and other hormones. During menopause, declining estrogen levels can make women more susceptible to DHT-related hair loss.
Spironolactone for hair loss is often the preferred DHT blocker for women. This medication blocks androgen receptors and reduces DHT production, making it effective for androgenetic alopecia in women while being safer during reproductive years.
Women’s hair loss treatment often requires a comprehensive approach addressing hormonal balance, nutritional factors, and stress management alongside DHT blockers safe for women.
FAQ for DHT Blockers Explained How They Work and Effectiveness for Hair Loss
What is DHT and how does it cause hair loss?
DHT is a hormone derived from testosterone that binds to hair follicles, shrinking them and causing hair loss over time.
What are DHT blockers and how do they work?
They inhibit the enzyme that converts testosterone to DHT, helping to protect follicles and encourage hair growth.
Are DHT blockers effective for treating hair loss?
Yes, especially prescription options like Finasteride and Dutasteride, which significantly reduce DHT levels.
What are the common side effects of DHT blockers?
Sexual dysfunction, skin irritation, and in rare cases, hormonal imbalances or liver enzyme changes.
Can women use DHT blockers for hair loss?
Some DHT blockers may be used by women, but only under strict medical guidance due to hormonal effects.
What are some natural DHT blockers?
Saw palmetto, green tea, pumpkin seed oil, and zinc are popular natural choices.
How long does it take for DHT blockers to show results?
Results typically appear within 3 to 6 months, with full benefits seen at around one year.
Are there alternatives to DHT blockers for hair loss treatment?
Yes, including Minoxidil, hair transplants, laser therapy, and scalp microneedling.