Genetic hair loss affects millions of people worldwide, making it one of the most common forms of hair thinning and baldness. Understanding how genetics influence hair loss can help you recognize early signs, explore treatment options, and make informed decisions about managing this hereditary condition. This comprehensive guide explores the science behind genetic hair loss, from the specific genes involved to the mechanisms that cause hair follicles to gradually shrink and stop producing hair.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Genetic Hair Loss?
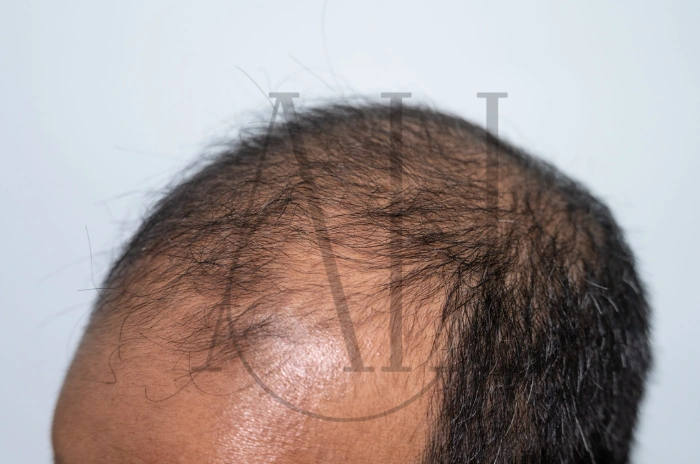
Genetic hair loss, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most prevalent cause of hair thinning in both men and women. This hereditary condition accounts for approximately 95% of male hair loss and is responsible for significant hair thinning in about 40% of women by age 50. Unlike temporary hair loss conditions, genetic hair loss is progressive and permanent without treatment.
The condition follows predictable patterns that distinguish it from other types of hair loss. In men, it typically begins with a receding hairline and thinning at crown male pattern, eventually progressing to partial or complete baldness. Women with genetic hair loss usually experience diffuse thinning across the top of the scalp while maintaining their hairline.
Androgenetic alopecia is fundamentally different from conditions like genetic hair loss vs telogen effluvium. While telogen effluvium causes temporary, widespread hair shedding due to stress or illness, genetic hair loss is a lifelong condition that worsens over time. The key distinction lies in the underlying cause: genetic hair loss results from inherited sensitivity to hormones, while telogen effluvium stems from external factors disrupting the hair growth cycle.
This type of hereditary hair loss can begin as early as the late teens or early twenties, though it more commonly becomes noticeable in the thirties and forties. The severity and timing of hair loss depend on the specific genetic variants inherited from both parents, making each person’s experience unique.
The Science Behind Hereditary Hair Loss
The biological mechanisms driving genetic hair loss involve complex interactions between hormones, genetic factors, and hair follicle biology. At the center of this process is dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a powerful hormone derived from testosterone through the action of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase.
DHT hair loss occurs when hair follicles inherit sensitivity to this hormone. DHT binds to androgen receptors in genetically susceptible hair follicles, triggering a cascade of cellular changes that gradually damage the follicle’s ability to produce healthy hair. This process doesn’t happen overnight but occurs over months and years, explaining why hereditary hair loss is progressive.
The hormone’s effects on hair follicles are particularly pronounced in specific areas of the scalp. The frontal hairline, temples, and crown region contain hair follicles with the highest concentration of androgen receptors and 5-alpha reductase enzyme. This explains why these areas are typically the first to show signs of thinning in male pattern baldness.
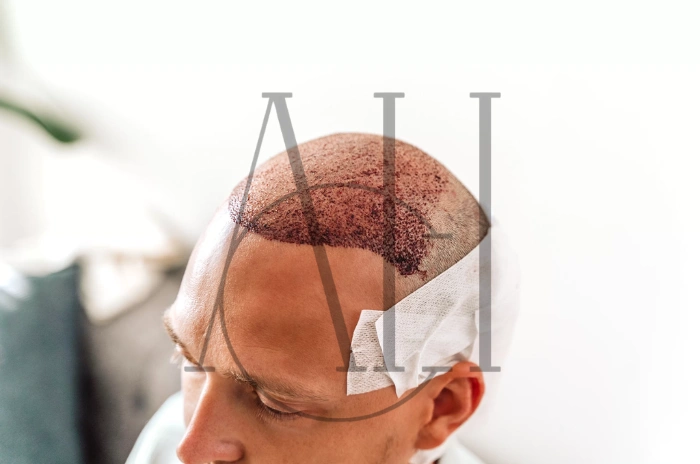
Interestingly, hair follicles in the back and sides of the scalp are generally resistant to DHT’s effects. This natural resistance is why these areas often retain hair even in advanced cases of genetic hair loss, making them ideal donor sites for hair transplant procedures.
Male vs. Female Pattern Baldness: How Genetics Differ
Male pattern baldness and female pattern hair loss share the same underlying genetic mechanisms but manifest differently due to hormonal and genetic variations between sexes. Understanding these differences is crucial for recognizing and treating each type of genetic hair loss.
| Characteristic | Male Pattern Baldness | Female Pattern Hair Loss |
|---|---|---|
| Pattern of Hair Loss | Receding hairline, crown thinning, M-shaped pattern | Diffuse thinning across top of scalp, preserved hairline |
| Age of Onset | Late teens to early twenties | Thirties to forties, accelerates after menopause |
| Severity | Can progress to complete baldness | Rarely progresses to complete baldness |
| Hormonal Influence | High testosterone and DHT levels throughout life | Protected by estrogen, worsens when estrogen declines |
| Genetic Inheritance | X chromosome from mother plays major role | Both X chromosomes contribute, more complex inheritance |
| Affected Population | 50% by age 50, 80% by age 80 | 40% by age 50, 65% by age 80 |
| Classification Scale | Hamilton-Norwood Scale (7 stages) | Ludwig Scale (3 stages) |
| Treatment Response | Good response to finasteride and dutasteride | Limited response to anti-androgens, minoxidil preferred |
In men, androgenetic alopecia typically follows the Hamilton-Norwood scale, beginning with temple recession and progressing to crown thinning. The thinning at crown male pattern often develops simultaneously with frontal hairline recession, creating the characteristic “M” shape that progresses to more extensive baldness. Men generally experience more severe hair loss because they have higher levels of testosterone and DHT.
Female pattern hair loss presents as diffuse thinning across the top of the scalp, following the Ludwig scale classification. Women rarely develop the severe baldness seen in men, partly due to lower androgen levels and higher estrogen levels that provide some protection against DHT hair loss. The condition often becomes more noticeable after menopause when estrogen levels decline.
Genetic Hair Loss Reasons
-
Family history of hair loss
-
Sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
-
Hormonal changes
-
Aging and reduced follicle activity
Understanding hair loss genetic inheritance helps determine risk levels and choose appropriate treatment plans. If both parents experience hair thinning, the likelihood of inheritance increases. Genetic testing can offer insight into your predisposition. Knowing your risks early opens the door for proactive care.
How To Stop Genetic Hair Loss?
While it’s difficult to completely stop genetic hair loss, early intervention can slow it down significantly. Several medically approved solutions are available today. It’s important to remain consistent with treatment. Ongoing evaluation ensures the chosen methods continue to be effective.
Minoxidil
A topical medication that increases blood flow to the hair follicles and prolongs the growth phase. It is FDA-approved for both men and women. Results typically appear after 3 to 6 months of consistent use. Side effects are minimal, mainly involving scalp irritation.
Finasteride
An oral medication that reduces DHT levels, slowing the progression of hair loss in men. It is generally not recommended for women. Finasteride has a strong track record of preserving hair density. Patients often see results within 3 to 12 months.
Which Genes Are Responsible for Hair Loss?
The genetics of hereditary hair loss involve multiple genes working together to determine susceptibility, timing, and severity. The most well-studied gene is the androgen receptor (AR gene hair loss), located on the X chromosome, which codes for the protein that DHT binds to in hair follicles.
The AR gene hair loss connection explains why men often inherit hair loss patterns from their mother’s side of the family. Since men receive their X chromosome from their mothers, they inherit the maternal androgen receptor gene variant. However, this doesn’t mean fathers don’t contribute to hair loss genetics – they certainly do through other genes.
Recent genome-wide association studies have identified over 300 genetic variants associated with androgenetic alopecia. Key genes include those involved in hair follicle development, hormone metabolism, and cellular signaling pathways. The EDA2R gene, WNT signaling pathway genes, and various genes controlling hair follicle cycling all contribute to genetic hair loss susceptibility.
The 5-alpha reductase genes (SRD5A1 and SRD5A2) are also crucial because they determine how much DHT is produced from testosterone. Variants in these genes can affect enzyme activity, influencing the severity of DHT hair loss in genetically susceptible individuals.
At What Age Does Genetic Hair Loss Start?
The onset of genetic hair loss varies considerably between individuals, but certain patterns emerge based on gender, family history, and specific genetic variants. Understanding these timelines can help people recognize early signs and seek appropriate treatment.
Male pattern baldness often begins in the late teens or early twenties, with about 20% of men showing some degree of hair loss by age 20. The progression typically accelerates during the twenties and thirties, with most men experiencing noticeable thinning by their forties. However, the severity varies greatly – some men develop significant baldness by their thirties, while others maintain most of their hair well into their sixties.
Female pattern hair loss generally starts later, with most women first noticing thinning in their thirties or forties. The condition often becomes more apparent during perimenopause and menopause when estrogen levels decline, reducing the protective effects against DHT hair loss. Some women may experience earlier onset, particularly those with strong family histories of hereditary hair loss.
Early signs of androgenetic alopecia include increased hair shedding during washing or brushing, gradual thinning at specific areas (temples and crown in men, diffuse thinning in women), and changes in hair texture. The hair may become finer, shorter, and lighter in color before eventually stopping growth altogether.
How to Know If Your Hair Loss Is Genetic
Distinguishing genetic hair loss from other causes of hair thinning is essential for choosing appropriate treatments. Several key characteristics help identify androgenetic alopecia versus conditions like alopecia areata, thyroid-related hair loss, or nutritional deficiencies.
Pattern recognition is the most reliable indicator of hereditary hair loss. In men, look for recession at the temples, thinning at crown male areas, or both occurring simultaneously. Women should watch for diffuse thinning across the top of the scalp while the hairline remains intact. These patterns are virtually diagnostic of genetic hair loss.
Family history provides crucial information. If parents, grandparents, or siblings experienced male pattern baldness or female pattern hair loss, genetic factors likely contribute to your hair loss. Remember that inheritance comes from both sides of the family, not just the mother’s side as commonly believed.
The progression timeline also offers clues. Androgenetic alopecia develops gradually over months and years, unlike sudden hair loss from medical conditions or treatments. The hair becomes progressively thinner and shorter in affected areas, eventually leading to miniaturized hairs that barely emerge from the scalp.
How Genes Lead to Hair Follicle Miniaturization
Hair follicle miniaturization is the hallmark of genetic hair loss, representing the gradual shrinkage of hair-producing structures due to genetic and hormonal influences. Understanding this process explains why hereditary hair loss is progressive and why early intervention is crucial for maintaining hair.
The miniaturization process begins when DHT binds to androgen receptors in genetically susceptible hair follicles. This binding activates cellular pathways that progressively damage the follicle’s structure and function. The dermal papilla, which controls hair growth, gradually shrinks, reducing its ability to nourish and support hair production.
As hair follicle miniaturization progresses, several changes occur in the affected follicles. The anagen (growth) phase becomes progressively shorter, while the telogen (resting) phase remains the same or lengthens. This means hair spends less time growing and more time in the dormant phase, resulting in shorter, thinner hairs.
The hair shaft itself undergoes changes during miniaturization. Normal terminal hairs, which are thick and pigmented, gradually transform into vellus-like hairs that are fine, short, and often unpigmented. Eventually, these miniaturized follicles may stop producing visible hair altogether, though they often remain alive at a microscopic level.
Modern genetic hair loss treatment approaches often target this miniaturization process. Finasteride for hair loss works by reducing DHT production, slowing the hormonal damage to follicles. Dutasteride hair loss treatment provides even more comprehensive DHT reduction by blocking both forms of the 5-alpha reductase enzyme.
Finding the Right Treatments for Genetic Hair Loss
Treating genetic hair loss requires a tailored approach. It’s important to understand the root cause before committing to a treatment plan. From over-the-counter medications to advanced surgical procedures, multiple solutions exist today. Choosing the right combination of methods can significantly improve outcomes. Consulting with a specialist can help you determine what’s best for your unique case.
Table: Genetic Hair Loss Treatments and Their Effectiveness
| Treatment Type | Best For | Success Rate | Invasiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minoxidil | Early-stage thinning | Moderate | Low |
| Finasteride | Male pattern baldness | High | Low |
| PRP Therapy | Diffuse thinning | Moderate | Low |
| FUE Transplant | Permanent bald spots | Very High | Moderate |
| Sapphire FUE | Precision hair restoration | Very High | Moderate |
FAQ :How Does Genetics Cause Hair Loss?
How do genetics cause male and female hair loss?
Genetics cause hair loss by creating sensitivity to DHT hormone in hair follicles, leading to progressive follicle miniaturization and eventual hair production cessation.
What specific genes are responsible for my hair loss?
The AR gene hair loss on the X chromosome is most important, along with over 300 other genetic variants affecting hormone metabolism and hair follicle development.
Can you prevent hereditary hair loss from starting?
While you cannot prevent genetic hair loss entirely, early treatment with medications like finasteride or dutasteride can significantly slow progression and maintain existing hair.
At what age does genetic hair loss begin?
Male pattern baldness often starts in the late teens or twenties, while female pattern hair loss typically begins in the thirties or forties, with timing influenced by family history and individual genetic factors.