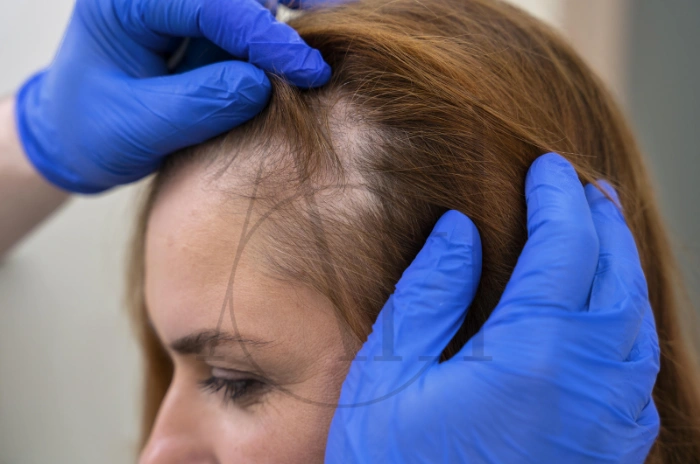
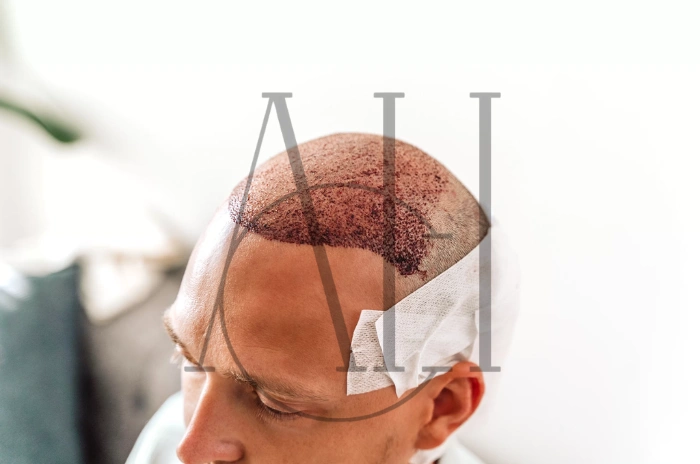
Hair loss affects millions of people worldwide, causing not only physical changes but also emotional distress. From genetic hair loss to stress-related hair thinning, understanding the root causes has become crucial for developing effective treatments. Recent hair loss research has unveiled promising new hair loss treatments that could revolutionize how we approach baldness and alopecia. This comprehensive guide explores the latest scientific breakthroughs, proven hair loss treatments, and practical strategies for maintaining healthy hair growth.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Causes Hair Loss?
| Hair Loss Type | Main Cause | Affected Area | Reversibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic Hair Loss | DHT hormone sensitivity | Crown, hairline | Partially treatable |
| Alopecia Areata | Autoimmune attack | Round patches | Often reversible |
| Telogen Effluvium | Stress/illness trigger | Diffuse thinning | Usually reversible |
| Traction Alopecia | Tight hairstyles | Hairline, temples | Early stages reversible |
Genetics and Hormones (e.g. DHT for pattern baldness)
Genetic hair loss, also known as androgenetic alopecia, represents the most common form of hair loss affecting both men and women. This condition stems from sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone derived from testosterone. DHT binds to hair follicle receptors, gradually shrinking them and shortening the hair growth cycle.
Autoimmune Hair Loss (Alopecia Areata)
Autoimmune hair loss occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy hair follicles. Alopecia areata causes include genetic predisposition combined with environmental triggers. This condition manifests as round, smooth patches of complete hair loss.
Triggered Hair Loss (Telogen or Anagen Effluvium)
Telogen effluvium represents temporary hair fall caused by physical or emotional stress. Major surgery, childbirth, or severe illness can push hair follicles into the resting phase prematurely. Stress hair loss from chronic psychological pressure also contributes to this condition.
Damage from Hairstyles or Scalp Issues
Hair loss from traction develops when excessive tension is repeatedly applied to hair strands. Scalp conditions hair loss includes inflammatory disorders that create an unhealthy environment for hair growth.
How Is Hair Loss Diagnosed?
Scalp Examination and Pull Test
Professional diagnosis begins with a thorough scalp examination by a dermatologist. The pull test involves gently tugging approximately 60 hairs to assess how many come loose. More than 6-8 hairs suggest active hair loss.
Dermoscopy allows detailed visualization of hair shaft characteristics and follicle patterns. This non-invasive technique helps distinguish between different types of alopecia and guides treatment decisions.
Blood Tests and Scalp Biopsy
Comprehensive blood work evaluates hormonal imbalances, nutritional deficiencies, and autoimmune markers that could contribute to hair loss. Tests typically include thyroid function, iron levels, vitamin D, and DHT measurements.
Scalp biopsy provides definitive diagnosis for complex cases. This procedure examines follicle structure and inflammation patterns, particularly useful for distinguishing scarring from non-scarring alopecia.
Conventional Treatments Available Today
| Treatment Type | How It Works | Success Rate | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minoxidil | Increases blood flow to follicles | 60-70% effectiveness | Scalp irritation, unwanted hair |
| Finasteride | Blocks DHT hormone | 80-90% halt progression | Rare sexual side effects |
| JAK Inhibitors | Suppresses immune attack | 50-80% regrowth in alopecia | Increased infection risk |
| Hair Transplant | Relocates healthy follicles | 90-95% graft survival | Scarring, temporary shock loss |
FDA‑approved Medications: Minoxidil, Finasteride, JAK inhibitors
Minoxidil remains the most widely used topical hair loss medication. Available over-the-counter in 2% and 5% concentrations, it promotes hair growth by increasing blood flow to follicles.
Finasteride, an oral medication for men, blocks DHT production and significantly slows genetic hair loss progression. JAK inhibitors represent a breakthrough for autoimmune hair loss, suppressing the immune system’s attack on hair follicles.
Laser Therapy and PRP Injections
Laser therapy for hair loss uses low-level light to stimulate cellular metabolism in hair follicles. PRP for hair loss involves injecting concentrated platelets from the patient’s blood into the scalp.
Hair Transplants and Surgical Options
Hair transplant procedures have evolved with techniques like FUE and FUT. Modern surgical hair restoration achieves natural-looking results by carefully placing individual follicles.
Promising New Research & Treatments
Stem Cell-Based Therapies & Exosomes
Stem cell hair growth research focuses on regenerating damaged follicles using mesenchymal stem cells. Exosomes hair loss treatment uses tiny vesicles derived from stem cells to deliver growth factors directly to follicles.
Deoxyribose Sugar: A Drug-Free Discovery
Recent research identified deoxyribose sugar as a drug-free hair loss treatment. This naturally occurring compound appears to stimulate hair regeneration without side effects.
What the Research Means for Patients
When Regrowth Is Likely (non‑scarring vs scarring types)
Hair regeneration prospects depend heavily on follicle damage extent. Non-scarring alopecia types maintain follicle structure, allowing potential regrowth with appropriate treatment.
Safety, Side Effects, and Future Availability
Current hair loss treatments generally show good safety profiles when properly administered. Future hair loss treatments focus on improving efficacy while minimizing adverse effects.
Lifestyle and Diet Tips to Support Hair Health
| Nutrient | Function for Hair | Best Food Sources | Daily Needs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iron | Oxygen transport to follicles | Red meat, spinach, lentils | 18mg (women), 8mg (men) |
| Biotin | Keratin protein synthesis | Eggs, nuts, sweet potatoes | 30-100mcg |
| Vitamin D | Follicle cycle regulation | Fatty fish, fortified foods | 600-800 IU |
| Zinc | Protein synthesis support | Oysters, pumpkin seeds | 8-11mg |
Reduce Mercury, Sugar, Smoking, and Manage Stress
Mercury exposure may contribute to hair loss. Excessive sugar creates inflammation, while smoking reduces circulation. Stress hair loss management requires holistic lifestyle changes.
How to Prevent Further Hair Loss
The Right Hair Care Routine (Shampoos, Heat Styling)
Gentle hair care prevents additional hair loss from traction and damage. Sulfate-free shampoos and lukewarm water protect the scalp’s natural barrier. Limiting heat styling and chemical treatments reduces hair shaft damage.
Foods That Fight Hair Loss (Protein, Omega-3s, Iron)
Adequate protein intake supports hair structure since hair consists primarily of keratin protein. Omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation and support healthy hair growth.
Stress Management Tips (Sleep, Exercise, Mindfulness)
Quality sleep allows cellular repair necessary for hair regeneration. Regular exercise improves circulation and reduces stress hormones that cause stress hair loss.
FAQ : Hair Loss; Causes and Treatments
What are the main causes of hair loss?
The primary causes include genetic predisposition to DHT sensitivity, autoimmune conditions like alopecia areata, stress-induced telogen effluvium, and damage from tight hairstyles or scalp conditions.
What are the current FDA-approved treatments?
Current treatments include topical minoxidil, oral finasteride, JAK inhibitors for autoimmune types, laser therapy, PRP injections, and surgical hair restoration procedures.
Which dietary changes can support reduce loss?
Focus on adequate protein, iron, biotin, vitamin D, and zinc intake while reducing mercury exposure, sugar, smoking, and managing chronic stress effectively.
What are common hair loss myths?
Common myths include hat-wearing causing baldness (false), complete hair loss reversal being always possible (depends on type), and head shaving affecting growth rate (false).