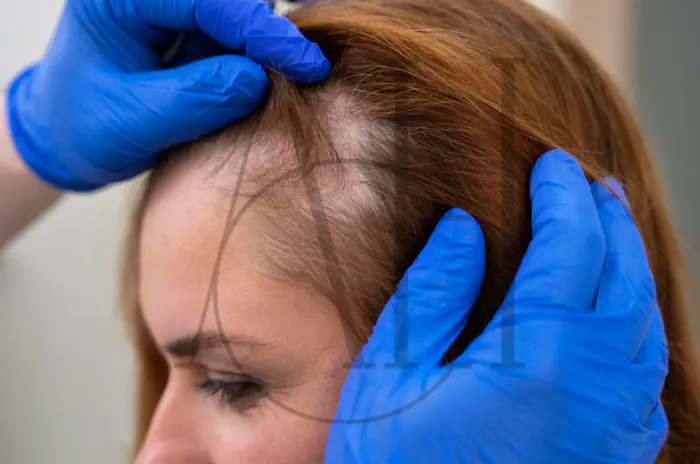
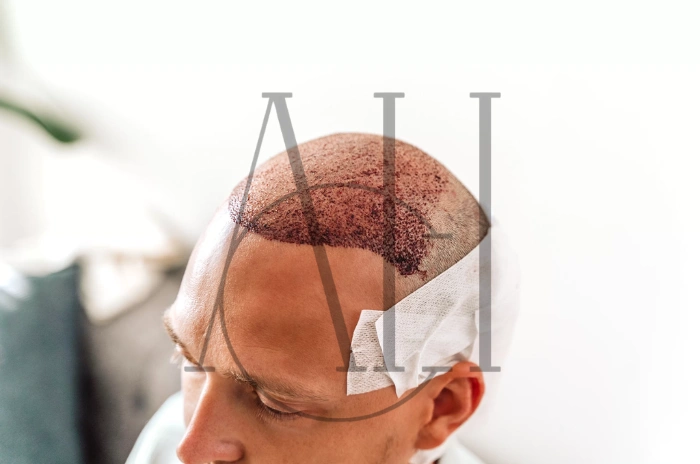
At Albania Hair intermediary organization, we believe that successful hair restoration is not just about medical treatments but also about effective counseling. Proper guidance helps patients understand their condition, set realistic expectations, and commit to a personalized plan that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of hair loss.
In this article, we will explore the causes of hair loss, its impact, how to counsel patients effectively, treatment options, daily care tips, and common FAQs.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Causes Hair Loss?
Hair loss has multiple causes, and often more than one factor is involved in each individual. Below is a table summarizing the most common causes and their patterns.
| Category | Examples | Typical Pattern | Diagnostic Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hormonal/Genetic | Androgenetic alopecia (DHT sensitivity), menopause, postpartum | Men: receding hairline/crown thinning; Women: diffuse crown thinning | Family history, scalp mapping, dermoscopy, hormone testing |
| Metabolic/Endocrine | Hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, insulin resistance, PCOS | Diffuse thinning | TSH, FT4, ferritin, fasting glucose/insulin |
| Telogen Effluvium | Stress, illness, surgery, rapid weight loss | Sudden, diffuse shedding | Timeline: triggers 2–3 months before onset |
| Inflammatory/Autoimmune | Alopecia areata, scarring alopecia | Patchy bald spots or permanent hair loss | Dermatology referral, possible biopsy |
| Drug/Lifestyle-Induced | Retinoids, anabolic steroids, certain progestins, tight hairstyles | Diffuse or traction-related | Medication history, hair practices |
| Nutritional Deficiencies | Low ferritin, vitamin D, zinc, protein | Weak hair shafts, brittle nails | Ferritin, CBC, dietary assessment |
Key point: It’s possible for a patient to have both a genetic predisposition and a temporary trigger (e.g., androgenetic alopecia with telogen effluvium after illness).
Understanding Hair Loss and Its Impact
Hair plays a vital role in identity and self-image. Hair loss can have far-reaching consequences beyond aesthetics.
Emotional Impact:
-
Loss of confidence
-
Anxiety or depression
-
Avoidance of social situations
Behavioral Impact:
-
Overuse of hair products and treatments
-
Wearing hats or tight hairstyles to hide thinning
-
Frequent comparison with others
Medical Impact:
-
Delayed treatment due to denial
-
Use of unverified or harmful products
-
Lack of consistent follow-up
Counseling Goal: Provide accurate information, clarify misconceptions, and design a care plan that fits the patient’s lifestyle and expectations.
How to Counsel Patients with Hair Loss
Albania Hair intermediary organization uses a structured approach to ensure patients feel informed, supported, and involved in their care.
1. Framing the Cause
-
Use neutral, non-blaming language:
“Your hair follicles are more sensitive to DHT due to genetics—this is not your fault.” -
Avoid medical jargon; explain terms in plain English.
2. Managing Expectations
-
Give a clear timeline:
-
Initial signs of improvement: 3–4 months
-
Noticeable results: 6–9 months
-
Full results: 9–12+ months
-
-
Focus on percentage improvements, not promises of complete reversal.
-
Emphasize maintenance: many treatments work only while being used.
3. Shared Decision-Making
-
Compare options in terms of benefits, risks, and costs.
-
Ask about personal priorities: Is speed of results important? Is low side-effect risk preferred?
-
Adjust plan based on pregnancy plans, lifestyle, or existing health conditions.
4. Action Planning
-
Start with 1–2 core actions:
-
Example: “Apply 5% minoxidil once daily + use LLLT 3 times/week.”
-
Example: “Correct low ferritin with supplements; recheck in 8 weeks.”
-
5. Objective Tracking
-
Take standard photos from the same angles, lighting, and distance.
-
Review every 12 weeks and adjust the plan as needed.
Counseling Do’s & Don’ts Table:
| Do | Don’t |
|---|---|
| Give a clear results timeline | Promise quick or guaranteed fixes |
| Recommend combination approaches | Rely solely on one product |
| Use measurable progress tools | Judge only by patient’s subjective feelings |
| Use simple, clear explanations | Overwhelm with medical jargon |
| Identify lifestyle obstacles | Ignore patient’s daily routine |

Best Treatment Options for Hair Loss
The choice of treatment depends on the cause, severity, gender, medical history, and patient goals. Here’s a comparison of the main options:
| Treatment | Mechanism | Ideal Candidates | Time to Notice | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topical Minoxidil (2–5%) | Extends growth phase, enlarges follicles | Men & women | 3–6 months | Possible initial shedding; consistent use is key |
| Oral Minoxidil (low dose) | Systemic stimulation | Those intolerant to topical | 3–6 months | Requires medical supervision |
| 5-alpha Reductase Inhibitors (Finasteride/Dutasteride) | Lowers DHT | Men, postmenopausal women | 4–6+ months | Requires discussion of side effects |
| Spironolactone | Blocks androgens | Women with androgen sensitivity | 3–6 months | Monitor potassium; not for pregnancy |
| PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) | Delivers growth factors | Early–moderate loss | 3–6 months | Series of sessions + maintenance |
| Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) | Stimulates follicles with light | Men & women | 3–6 months | Consistency critical |
| Endocrine Management | Corrects hormonal imbalances | Thyroid, PCOS, high prolactin | Variable | Targets root cause |
| Nutritional Optimization | Corrects deficiencies | All patients | 2–3 months | Focus on iron, vitamin D, protein |
| Hair Transplant | Moves DHT-resistant hair | Stable pattern loss | 9–12 months | Requires medical maintenance of surrounding hair |
Example Female Plan:
-
Minoxidil 5% once daily
-
LLLT 3x/week
-
Iron supplementation if ferritin <40 ng/mL
-
PCOS management if present
Example Male Plan:
-
Oral finasteride + topical minoxidil
-
PRP series + LLLT
-
Hair transplant if advanced, combined with medical therapy
Understanding Hair Loss and Its Impact (Deeper Dive)
This section focuses on patient education and motivation.
Educational Elements:
-
Explain the hair growth cycle (Anagen–Catagen–Telogen).
-
Describe miniaturization and why early treatment matters.
-
Reinforce patience:
“You might notice shedding before improvement—that’s a sign of follicles resetting.”
Motivational Strategies:
-
Ask: “How important is it for you to follow this plan on a scale of 1–10?”
-
Identify obstacles: “What could prevent you from applying your treatment daily?”
-
Offer solutions: Reminders, simplified routines, or alternative products.
Plateau or Relapse Management:
-
If no progress after 3–6 months, review adherence, dosage, and combination strategies.
-
If side effects occur, adjust the plan without losing progress.
Daily Hair Care and Self-Management Tips
Gentle Hair Care:
-
Use mild shampoos without harsh sulfates.
-
Limit high-heat styling and harsh chemical treatments.
-
Avoid tight hairstyles that pull on the hairline.
-
Protect scalp from UV damage with hats or sunscreen sprays.
Nutrition & Lifestyle:
-
Include protein (1.0–1.2 g/kg/day), iron-rich foods, zinc, vitamin D, and omega-3s.
-
Avoid crash diets—sudden calorie restriction can cause shedding.
-
Sleep 7–9 hours nightly; manage stress with exercise, meditation, or breathing exercises.
Monitoring & Maintenance:
-
Apply treatments at the same time daily.
-
Take monthly progress photos in consistent lighting.
-
Address any scalp irritation early to prevent treatment interruption.
FAQ
What causes my hair loss?
Common causes include genetic sensitivity to DHT (androgenetic alopecia), hormonal changes (menopause, postpartum), thyroid issues, PCOS, stress, medications, and nutritional deficiencies. Multiple causes may occur together.
What are the best treatment options?
The most effective plans combine topical/oral minoxidil, DHT blockers, anti-androgens (for women), PRP, LLLT, endocrine correction, and nutrition optimization. In advanced stable cases, hair transplantation can be combined with medical maintenance.
How long does it take for results?
Usually 3–4 months for early signs, 6–9 months for noticeable improvement, and 9–12 months for full results. Timelines vary depending on the cause and treatment combination.
How will my hair loss affect me?
Hair loss can affect confidence, mood, and social interactions. Counseling, realistic expectations, and supportive care help minimize emotional and social impact.