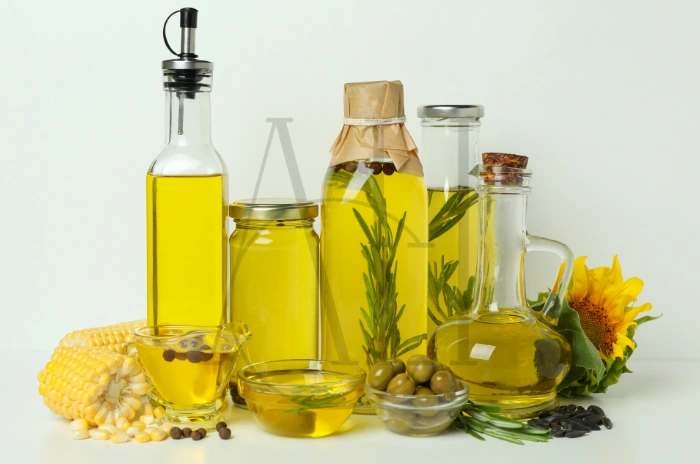
The world of hair oil effectiveness is filled with conflicting claims and marketing hype, leaving many wondering which oils actually deliver on their promises. While countless products claim to repair damaged hair, scientific research reveals that not all oils are created equal when it comes to hair oil penetration science.
Understanding the difference between oils that genuinely penetrate the hair shaft versus those that simply coat the surface is crucial for making informed decisions about your hair care routine. Recent hair oil benefits research has identified specific molecular characteristics that determine whether an oil can truly repair hair from within or merely provide surface protection.
This comprehensive guide examines the scientific evidence hair oil provides, breaking down which formulations offer proven results and which fall short of their claims.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Hair Oil Types: Penetrating vs. Sealing
The fundamental distinction in hair oil absorption studies lies between oils that penetrate the hair shaft and those that seal the cuticle layer. This difference determines whether an oil can provide internal hair oil damage repair or simply offers surface protection and shine.
Penetrating oils possess specific molecular characteristics that allow them to move through the hair cuticle and into the cortex, where they can interact with hair proteins and provide structural support. These oils typically contain smaller molecules with specific fatty acid profiles that enable deeper absorption.
What makes an oil “penetrating”? (molecular size, triglycerides)
Hair oil molecular penetration depends primarily on molecular size and fatty acid composition. Oils with smaller molecular structures can more easily navigate through the hair cuticle’s microscopic gaps and reach the inner cortex where repair occurs.
Triglyceride structure plays a crucial role in penetration ability. Oils containing medium-chain fatty acids, particularly those with 12-14 carbon atoms, demonstrate superior penetration compared to longer-chain alternatives.
Sealing oils: how they coat and protect hair
Sealing oils create a protective film on the hair’s outer cuticle layer, providing barrier protection without significant internal penetration. These oils typically contain larger molecules that prevent deep absorption while offering surface benefits.
The protective coating formed by sealing oils helps retain moisture within the hair shaft by reducing water loss. This mechanism proves particularly beneficial for dry, damaged, or chemically processed hair.
Which Oils Actually Penetrate and Repair Hair
Hair Oil Penetration and Benefits Comparison
| Oil Type | Primary Fatty Acid | Molecular Weight | Penetration Level | Main Benefits | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coconut Oil | Lauric Acid (C12) | 200 Da | High | Protein retention, strengthening, damage repair | Damaged, chemically processed hair |
| Olive Oil | Oleic Acid (C18:1) | 282 Da | Moderate | Moisture, flexibility, split end sealing | Dry, brittle hair |
| Avocado Oil | Oleic Acid (C18:1) | 280 Da | Moderate | Deep hydration, vitamin E protection | Thick, coarse hair |
| Jojoba Oil | Eicosenoic Acid | 338 Da | Moderate | Scalp health, sebum regulation | Oily scalp, fine hair |
| Argan Oil | Oleic/Linoleic Acids | 450+ Da | Low | Shine, smoothing, antioxidant protection | Color-treated, frizzy hair |
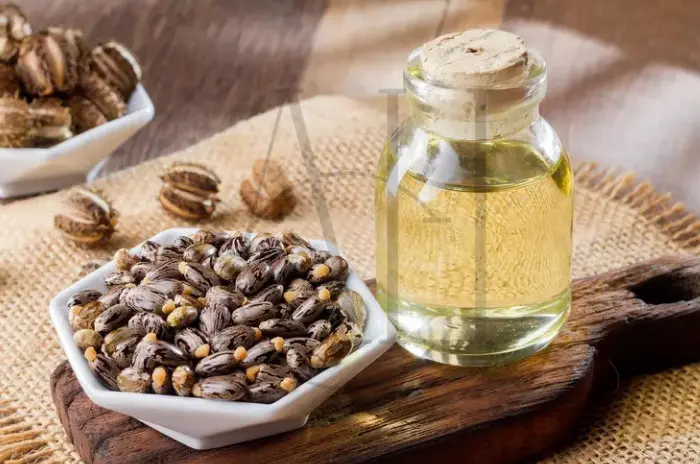
| Castor Oil | Ricinoleic Acid | 298 Da | Low | Thickness, growth stimulation, protection | Thin hair, scalp treatments |
| Grapeseed Oil | Linoleic Acid | 280 Da | Low | Light conditioning, antioxidants | Fine, oily hair |
Proven hair oil results from scientific studies have identified specific oils capable of genuine hair shaft penetration and internal repair. These oils demonstrate measurable improvement in hair strength, protein retention, and overall structural integrity through documented research.
Coconut oil – lauric acid, protein retention & study-backed efficacy
Coconut oil stands as the most scientifically validated penetrating oil, with extensive research demonstrating its ability to prevent protein loss and strengthen hair fibers. The high concentration of lauric acid enables effective penetration through the hair cuticle.
Studies published in the Journal of Cosmetic Science show that coconut oil reduces protein loss by up to 39% when used as a pre-wash treatment. This scientific evidence hair oil effectiveness stems from lauric acid’s affinity for hair proteins.
Avocado & olive oils – monounsaturated fats and deep hydration
Avocado and olive oils contain high concentrations of monounsaturated fats, particularly oleic acid, which demonstrates moderate penetration ability and excellent moisturizing properties. These oils provide hair oil benefits research has shown to include improved flexibility and reduced brittleness.

Oils That Reinforce but Don’t Penetrate Deeply
Many popular hair oils function primarily as sealing agents rather than penetrating treatments, providing valuable protective benefits without significant internal repair capabilities.
Argan, castor, grapeseed, and jojoba as sealing oils
Argan oil contains predominantly oleic and linoleic acids with larger molecular structures that limit deep penetration while providing excellent surface conditioning. Hair oil clinical studies show that argan oil excels at cuticle smoothing and moisture retention.
Castor oil’s high ricinoleic acid content creates a thick, protective coating that helps retain moisture and provides mechanical protection against damage.
Carrier Oil Chemistry: What Determines Penetration
The molecular chemistry underlying hair oil molecular penetration involves complex interactions between fatty acid structure, molecular size, and hair fiber composition.
Chain length, saturation, molecular polarity
Medium-chain fatty acids (8-14 carbons) demonstrate superior hair penetration compared to longer-chain alternatives due to their smaller molecular size. Scientific evidence hair oil research shows that lauric acid (C12) and myristic acid (C14) penetrate most effectively.
Saturated fatty acids provide better penetration than unsaturated alternatives due to their linear molecular structure, which allows easier movement through hair fiber gaps.
Short-chain vs. long-chain fatty acids
Short-chain fatty acids offer the highest penetration potential but may lack sufficient substantivity to provide lasting benefits. Medium-chain fatty acids provide optimal balance between penetration ability and retention within hair fibers.
Best Hair Oils for Repairing Damaged Hair
Coconut Oil – Deep Penetration & Protein Retention
Coconut oil remains the gold standard for hair oil damage repair due to its proven ability to penetrate hair shafts and prevent protein loss. The high lauric acid content enables deep absorption and binding with hair proteins.
Argan Oil – Moisture & Shine Restoration
Argan oil excels at restoring moisture and shine to damaged hair through its rich vitamin E content and balanced fatty acid profile. The oil’s antioxidant properties help protect against ongoing environmental damage.
Olive Oil – Strengthening & Split End Repair
Olive oil’s high oleic acid content enables moderate penetration and excellent strengthening properties for damaged hair. Studies show that olive oil treatments can reduce hair breakage and improve tensile strength.

How to Choose the Right Hair Oil for Your Hair Type
Best Oils for Dry & Brittle Hair
Dry, brittle hair requires oils that provide both internal moisture and external protection. Penetrating oils like coconut and olive oil work best for addressing internal dryness.
Best Oils for Oily or Fine Hair
Fine or oily hair requires lighter oils that provide benefits without adding excess weight. Jojoba oil works well due to its similarity to natural sebum and ability to regulate oil production.
Best Oils for Curly or Coily Hair
Curly and coily hair types typically have higher porosity and benefit from richer oil combinations that provide intensive moisture and definition enhancement.
How to Use Hair Oils for Maximum Repair
Pre‑wash hot‑oil treatments with penetrating oils
Hot oil treatments enhance hair oil molecular penetration by temporarily opening hair cuticles and increasing oil fluidity for deeper absorption. Warming penetrating oils before application maximizes their repair potential.
Layering method: moisturize then seal
The layering method maximizes hair oil effectiveness by combining penetrating and sealing oils in strategic sequence. This approach addresses both internal repair and external protection.
Evidence-Based Benefits & Precautions
Reduction in protein loss & breakage (studies, Reddit confirmation)
Peer-reviewed research consistently demonstrates that penetrating oils, particularly coconut oil, significantly reduce protein loss and hair breakage. Studies show up to 39% reduction in protein loss with regular coconut oil use.
Potential downsides (greasiness, dandruff, buildup)
Excessive oil use can lead to greasiness, scalp irritation, and product buildup. Some individuals may experience increased dandruff with certain oils, particularly those prone to seborrheic dermatitis.
Scientific Explanation: How Oils Penetrate Hair Shafts
The Role of Molecular Size in Oil Penetration
Molecular size represents the primary factor determining whether oils can penetrate hair shafts. Scientific evidence hair oil research establishes clear correlations between molecular weight and penetration depth.
Why Some Oils Sit on the Surface (Sealing Oils)
Sealing oils contain predominantly large molecules that cannot penetrate hair cuticle barriers effectively. These oils provide valuable surface benefits including moisture retention and environmental protection.
FAQ : Hair Oil Repairs or Penetrates What Science Says About Effectiveness
What is the difference between “penetrating” and “sealing” hair oils?
Penetrating oils contain small molecules that can enter the hair shaft to repair from within, while sealing oils form protective barriers on the hair surface.
Which hair oils are considered “penetrating” and offer internal repair?
Coconut oil, olive oil, and avocado oil demonstrate proven penetration ability and internal repair benefits through scientific testing.
Which oils are considered “sealing” and best for coating and protecting hair?
Argan oil, castor oil, grapeseed oil, and jojoba oil primarily function as sealing agents that provide surface protection.
How do penetrating oils actually repair damaged hair?
Penetrating oils fill gaps in damaged cuticles, bind with hair proteins to prevent loss, and provide structural support from within.
Should I use penetrating oils, sealing oils, or both for my hair?
Most hair types benefit from both: penetrating oils for internal repair, followed by sealing oils for protection
How can I effectively use penetrating oils for maximum hair repair?
Apply to damp hair as pre-wash treatments, use gentle heat, and allow 20-60 minutes contact time before shampooing
Can using the wrong type of oil cause problems for my hair?
Yes, heavy oils on fine hair cause greasiness, while excessive penetrating oils can lead to protein overload and stiffness.
What’s the role of molecular size and fatty acid chains in oil penetration?
Smaller molecules and medium-chain fatty acids penetrate most effectively, while larger molecules remain on the surface.