Lupus hair loss affects millions of people worldwide, creating significant emotional and physical challenges for those managing this autoimmune condition. Understanding the connection between lupus and hair loss is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available for individuals experiencing lupus and hair loss treatment needs.
Autoimmune hair loss symptoms can vary significantly from person to person, making it essential to recognize the early warning signs. Whether you’re newly diagnosed with lupus or have been managing the condition for years, this article provides valuable insights into maintaining scalp health and exploring treatment options.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Lupus Hair Loss and Its Causes
Lupus hair loss occurs when the autoimmune system attacks healthy hair follicles, leading to inflammation and subsequent hair damage. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and discoid lupus are the two primary forms that directly impact hair growth and retention.
The inflammatory process characteristic of lupus creates an environment where hair follicles cannot function optimally. When the immune system mistakenly targets hair follicles as foreign invaders, it triggers inflammation that disrupts the natural hair growth cycle. This disruption can lead to both temporary and permanent hair loss patterns.
Medications commonly prescribed for lupus management can also contribute to hair loss from lupus. Corticosteroids, antimalarials, and immunosuppressants may cause hair thinning as a side effect. Additionally, the chronic stress associated with managing a long-term autoimmune condition can trigger telogen effluvium, a temporary form of diffuse hair loss.
Autoimmune hair loss mechanisms involve cytokine release, which creates inflammatory cascades affecting the hair follicle’s anagen (growth) phase. This process can shift hair follicles prematurely into the telogen (resting) phase, resulting in increased shedding and reduced hair density.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Lupus Hair Loss
Recognizing early symptoms of lupus hair loss enables timely intervention and better treatment outcomes. The initial signs often appear gradually, making them easy to overlook during routine grooming activities.
Increased hair shedding during washing or brushing represents one of the earliest indicators. While normal daily hair loss ranges from 50-100 strands, individuals with lupus symptoms hair involvement may notice 200-300 strands or more during routine activities.
Changes in hair texture often accompany increased shedding. Hair may become more brittle, dry, or prone to breakage. The scalp itself may feel tender or sensitive, particularly in areas where lupus scalp thinning is beginning to develop.
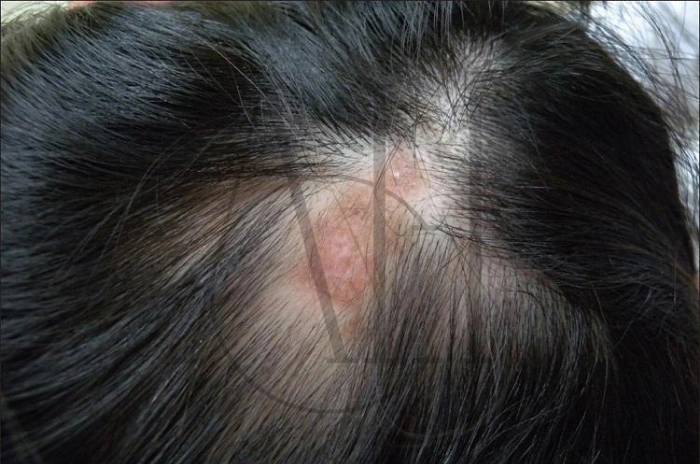
Patchy hair loss patterns distinguish lupus related alopecia from other forms of hair loss. Unlike male pattern baldness, which follows predictable patterns, lupus-related hair loss can occur in irregular patches across the scalp, creating a “moth-eaten” appearance.
Key Early Warning Signs Include:
- Excessive hair shedding during washing or styling
- Increased hair found on pillows, clothing, or shower drains
- Changes in hair texture, becoming more fragile or coarse
- Scalp sensitivity or tenderness in specific areas
- Irregular patchy hair loss patterns
- Reduced hair volume and density over time
Common Symptoms That Indicate Lupus Hair Loss
How to spot lupus hair loss requires understanding the distinctive characteristics that separate it from other hair loss conditions. Unlike androgenetic alopecia, lupus-related hair loss often presents with unique patterns and accompanying symptoms.
Diffuse hair loss represents the most common presentation, where hair thinning occurs uniformly across the entire scalp. This pattern differs from typical male or female pattern baldness, which tends to follow specific genetic patterns with predictable progression.
Scarring alopecia can occur in severe cases, particularly with discoid lupus. This form of lupus hair shedding signs involves permanent damage to hair follicles, resulting in smooth, shiny patches of scalp where hair cannot regrow naturally.
The “lupus hair” phenomenon describes short, broken hairs that appear around the hairline and temples. These fragile, wispy hairs typically measure 1-2 inches in length and break easily due to the inflammatory process affecting the hair shaft structure.
Distinctive Lupus Hair Loss Characteristics:
| Symptom Type | Description | Reversibility |
|---|---|---|
| Diffuse Thinning | Uniform hair loss across entire scalp | Often reversible |
| Patchy Loss | Irregular bald spots throughout scalp | Variable recovery |
| Scarring Alopecia | Permanent follicle damage with smooth patches | Irreversible |
| Broken Hairs | Short, fragile hairs around hairline | Reversible with treatment |
| Scalp Inflammation | Red, scaly, or tender scalp areas | Treatable |
Effective Treatments for Lupus Related Hair Loss
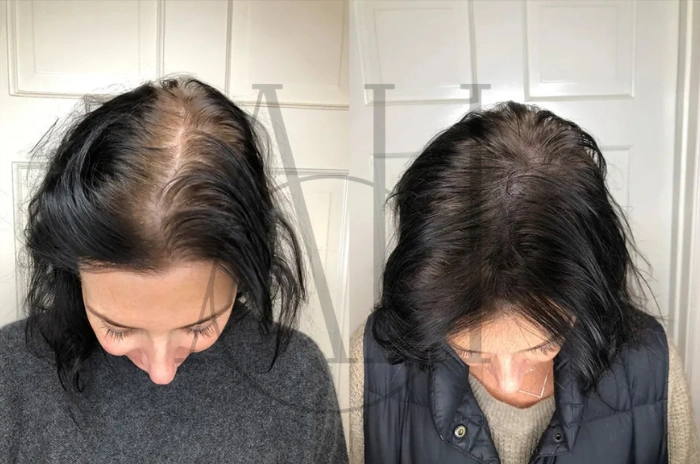
Treatment for lupus hair loss requires a comprehensive approach addressing both the underlying autoimmune condition and specific hair loss symptoms. Early intervention significantly improves the likelihood of lupus hair regrowth and prevents permanent follicle damage.
Topical corticosteroids represent the first-line treatment for lupus hair treatment protocols. These medications reduce local inflammation around hair follicles, allowing the natural growth cycle to resume. Clobetasol propionate and betamethasone valerate are commonly prescribed formulations.
Systemic treatments focus on controlling the underlying lupus activity. Hydroxychloroquine, an antimalarial medication, helps reduce overall disease activity and can indirectly improve hair loss outcomes. Methotrexate and other immunosuppressants may be necessary for severe cases.
DHT blockers hair treatments can provide additional benefits, particularly for individuals experiencing concurrent androgenetic alopecia. Finasteride and dutasteride help preserve existing hair while lupus-specific treatments address the autoimmune component.
Treatment Options by Severity:
Mild to Moderate Hair Loss:
- Topical corticosteroids (clobetasol, betamethasone)
- Minoxidil 2-5% solutions
- Anti-inflammatory shampoos with ketoconazole
- Gentle hair care practices
Severe or Progressive Hair Loss:
- Systemic corticosteroids (short-term use)
- Immunosuppressive medications (methotrexate, mycophenolate)
- Biologic therapies for refractory cases
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatments
How to Prevent Hair Breakage with Lupus
Scalp health lupus maintenance requires specialized care techniques that minimize additional trauma to already vulnerable hair follicles. Gentle hair care practices form the foundation of any effective prevention strategy.
Heat styling tools should be avoided or used minimally with protective products. High temperatures can further weaken hair shafts already compromised by inflammatory processes. Air-drying or using low-heat settings helps preserve hair integrity.
Chemical treatments including perms, relaxers, and frequent coloring can exacerbate hair thinning lupus symptoms. These processes create additional stress on fragile hair structures, potentially accelerating breakage and loss.
Lupus flare hair episodes require modified care routines. During active disease periods, gentle handling becomes even more critical. Wide-tooth combs, silk pillowcases, and protective hairstyles can minimize mechanical damage.
Daily Hair Care Recommendations:
- Use sulfate-free, pH-balanced shampoos
- Apply conditioner from mid-length to ends
- Detangle hair when wet using wide-tooth combs
- Avoid tight hairstyles that create scalp tension
- Protect hair from UV exposure with hats or scarves
- Limit washing frequency to 2-3 times per weekly
Nutritional support plays a crucial role in maintaining hair health during lupus management. Adequate protein intake, B-vitamins, iron, and zinc support hair follicle function and may help minimize hair shedding lupus episodes.
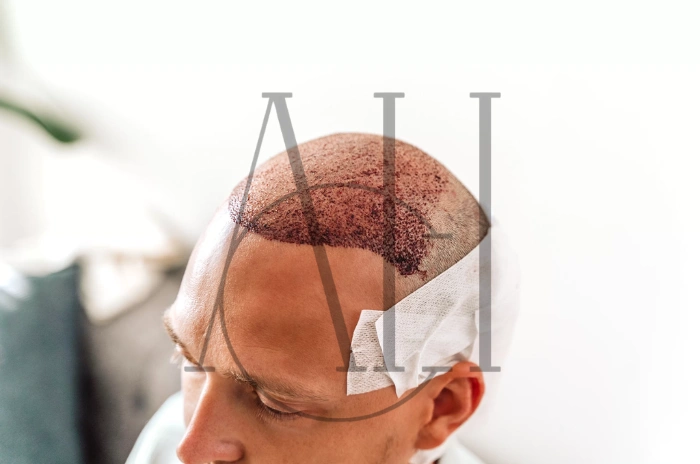
Hair Transplant After Stable Lupus FUE or DHI
Hair transplant lupus patients require careful evaluation and specialized planning to ensure optimal outcomes. The autoimmune nature of lupus creates unique considerations that must be addressed before surgical intervention.
Disease stability represents the most critical factor in hair loss diagnosis and treatment planning. Most surgeons require at least 12-18 months of stable lupus activity before considering transplantation procedures. This waiting period helps ensure the transplanted follicles won’t be attacked by the immune system.
FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) techniques often prove superior to traditional strip harvesting for lupus patients. The minimally invasive nature of FUE reduces surgical trauma and may lower the risk of triggering disease flares during the healing process.
DHI (Direct Hair Implantation) offers additional advantages for individuals with lupus related alopecia. The precise implantation technique minimizes tissue trauma and allows for more natural hair growth patterns, particularly important for those with irregular scarring patterns.
Pre-Transplant Requirements:
- Stable lupus activity for 12-18 months minimum
- Normal inflammatory markers (ESR, CRP)
- Adequate donor hair density and quality
- Realistic expectations about outcomes
- Comprehensive medical clearance from rheumatologist
Post-Transplant Considerations:
- Modified immunosuppressive protocols
- Enhanced wound care and monitoring
- Gradual return to normal hair care routines
- Long-term follow-up for disease monitoring
- Potential need for maintenance treatments
The success rates for hair transplantation in stable lupus patients approach those of the general population when proper precautions are taken. However, ongoing medical management and regular monitoring remain essential for maintaining both transplant results and overall health.
FAQ :Lupus hair loss causes symptoms and treatment options
What causes hair loss in people with lupus?
Lupus hair loss occurs when the autoimmune system attacks healthy hair follicles, causing inflammation that disrupts the normal hair growth cycle and leads to increased shedding and thinning.
Can hair loss from lupus be reversed?
Hair loss from lupus can often be reversed with appropriate treatment, especially when caught early, though scarring alopecia from discoid lupus may result in permanent hair loss in affected areas.
What are the key symptoms of lupus hair loss?
Early symptoms of lupus hair loss include excessive shedding during washing or brushing, patchy irregular hair loss patterns, brittle hair texture, and scalp sensitivity or tenderness.
Can a hair transplant fix permanent lupus hair loss?
Hair transplant lupus patients can achieve successful results when the disease has been stable for 12-18 months, though careful evaluation and specialized planning are essential for optimal outcomes.