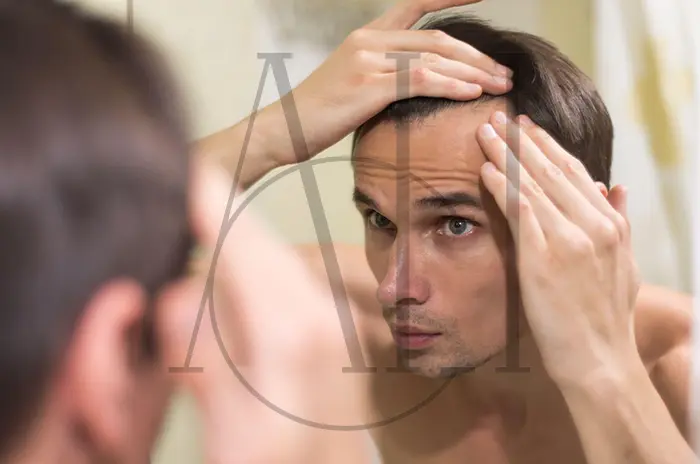
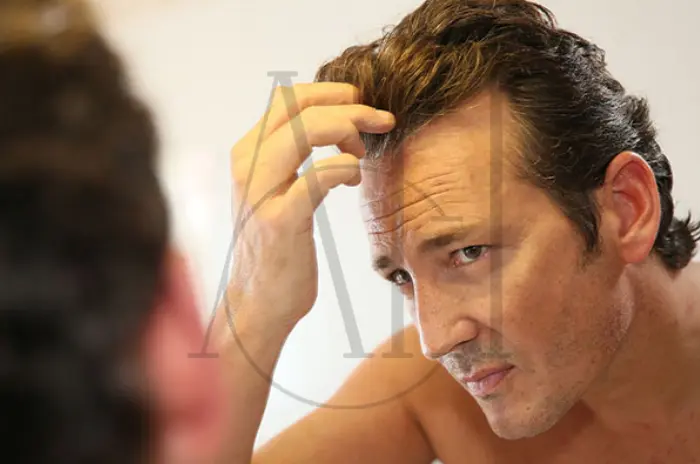
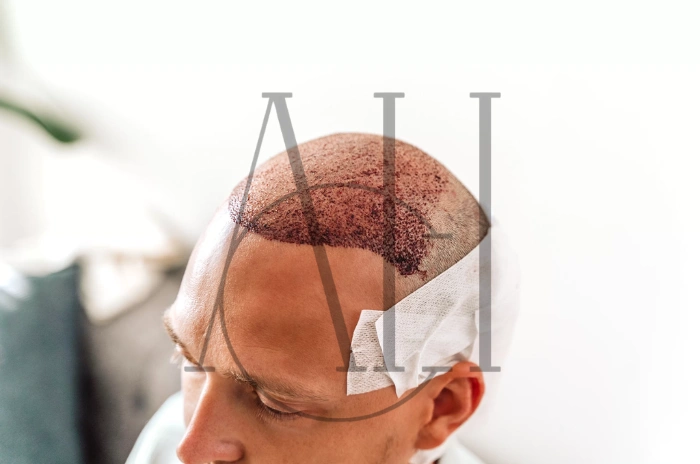
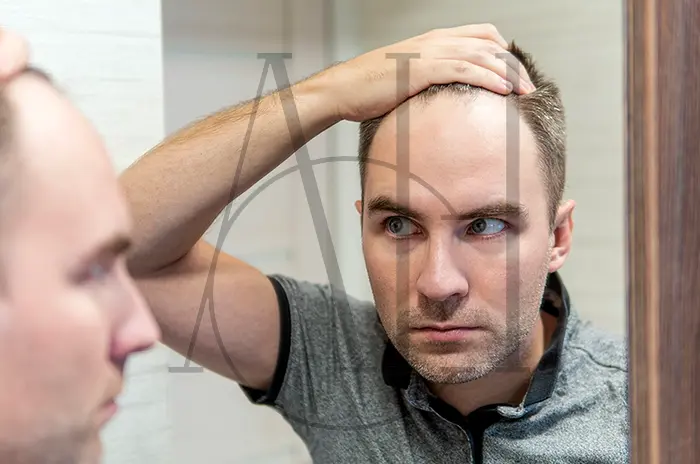
A receding hairline is one of the most common early signs of hair loss, affecting millions of men and women worldwide. This gradual retreat of the hairline can significantly impact self-confidence and appearance, leading many to seek effective solutions. At Albania Hair Clinic, our experienced intermediary organization understands the emotional and physical challenges associated with hairline recession and provides comprehensive treatment options tailored to each patient’s unique needs.
Understanding the causes, stages, and available treatments for receding hairlines empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their hair restoration journey. Early intervention often yields the best results, making education and awareness crucial components of successful hair loss management.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is a Receding Hairline?
A receding hairline refers to the gradual loss of hair from the front and sides of the scalp, creating a backward movement of the natural hairline. This condition typically begins at the temples and progresses toward the crown, forming characteristic patterns that vary between individuals.
Key characteristics include:
- Progressive hair loss from the frontal scalp
- Temple recession creating an “M” or “V” shape
- Gradual thinning of existing hair
- Miniaturization of hair follicles
- Eventual complete hair loss in affected areas
The process occurs gradually over months or years, making early detection and intervention crucial for preserving existing hair and preventing further progression.
Receding Hairline Causes
Multiple factors contribute to hairline recession, often working in combination to accelerate the hair loss process. Understanding these causes helps identify appropriate treatment strategies and preventive measures.
|
Cause Category |
Impact Level |
Reversibility |
Prevention Possible |
|
Genetics |
Very High |
Limited |
No |
|
Hormones |
High |
Moderate |
Partial |
|
Lifestyle |
Moderate |
High |
Yes |
|
Medical |
Variable |
Variable |
Sometimes |
Over-styling hair
Excessive manipulation and styling can cause significant damage to hair follicles, particularly along the delicate hairline. This mechanical stress leads to inflammation and eventual follicle miniaturization.
Damaging practices include:
- Tight ponytails and braids
- Excessive brushing or combing
- Frequent use of hair elastics
- Aggressive towel drying
- Rough handling when wet
Using chemicals (Bleach, Peroxide for color hair)
Chemical treatments can severely damage hair structure and follicles, especially when used repeatedly or improperly applied. The hairline is particularly vulnerable due to finer hair and more sensitive skin.
Common chemical culprits:
- Hair bleaching products
- Permanent hair dyes
- Chemical relaxers
- Perming solutions
- Harsh styling products
Eating a diet that’s high in saturated fat
Poor dietary choices can negatively impact hair health by affecting hormone levels, inflammation, and nutrient availability. High saturated fat intake has been linked to increased DHT production and follicle inflammation.
Dietary risk factors:
- Processed foods high in saturated fats
- Excessive sugar consumption
- Limited protein intake
- Inadequate vitamin and mineral consumption
- Poor hydration habits
Smoking
Tobacco use significantly impacts hair health through multiple mechanisms, including reduced blood circulation, increased oxidative stress, and accelerated aging processes.
Smoking effects on hair:
- Decreased blood flow to follicles
- Increased free radical damage
- Premature graying
- Accelerated hair loss progression
- Impaired healing and regrowth
Inflammatory scalp diseases
Various scalp conditions can cause inflammation that damages hair follicles and leads to permanent hair loss if left untreated.
Common conditions:
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Scalp psoriasis
- Folliculitis
- Lichen planopilaris
- Frontal fibrosing alopecia
Age
Natural aging processes affect hair growth cycles, follicle sensitivity, and overall hair health. Age-related changes become more pronounced after age 30.
Age-related factors:
- Decreased hair growth rate
- Increased DHT sensitivity
- Reduced follicle regeneration
- Hormonal fluctuations
- Cumulative damage effects
Hormonal changes
Hormonal fluctuations throughout life can significantly impact hair growth patterns and follicle health, particularly affecting the hairline.
Key hormonal influences:
- DHT (dihydrotestosterone) sensitivity
- Thyroid hormone imbalances
- Insulin resistance
- Cortisol elevation
- Sex hormone fluctuations
Family history
Genetic predisposition plays the most significant role in determining hairline recession patterns and timing. Family history from both maternal and paternal sides contributes to risk.
Genetic factors:
- Androgen receptor sensitivity
- 5-alpha-reductase activity
- Hair growth cycle duration
- Follicle miniaturization susceptibility
- Age of onset patterns
Illness or stress
Physical and emotional stress can trigger various forms of hair loss, including hairline recession through telogen effluvium and acceleration of androgenetic alopecia.
Stress-related triggers:
- Major illness or surgery
- Extreme weight loss
- Emotional trauma
- Chronic stress conditions
- Sleep deprivation
Genetics
Genetic factors determine the fundamental susceptibility to hairline recession and overall pattern of hair loss progression.
Inherited characteristics:
- DHT sensitivity levels
- Hair follicle structure
- Growth cycle patterns
- Enzyme activity levels
- Hormonal response patterns
Why Your Hairline Changes
The hairline represents one of the most sensitive areas of the scalp to hormonal and environmental influences. Several factors contribute to its particular vulnerability to hair loss.
Anatomical considerations:
- Thinner skin at the hairline
- Higher concentration of DHT receptors
- Increased mechanical stress
- Greater exposure to environmental damage
- Reduced blood circulation
Biological processes:
- Follicle miniaturization progression
- Decreased hair growth phases
- Increased shedding cycles
- Inflammation responses
- Cellular aging effects
The combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors creates a cascade of changes that progressively affect hairline integrity over time.

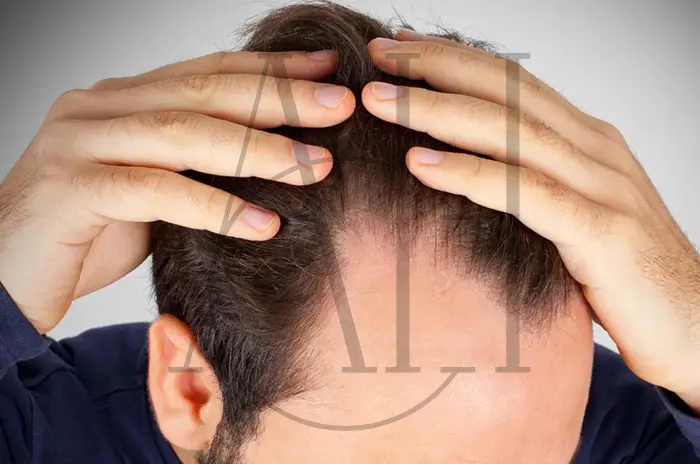
Signs of a Receding Hairline
Early recognition of hairline recession enables prompt intervention and better treatment outcomes. Several key indicators help identify the onset and progression of this condition.
Higher hairline
The most obvious sign is a gradual upward movement of the hairline, creating more forehead space than previously present.
Measurement indicators:
- Increased distance from eyebrows to hairline
- Comparison with old photographs
- Changes in hat or helmet fit
- Altered facial proportions
- Family member observations
M-Shape Pattern
The classic male pattern involves temple recession that creates a distinctive “M” or “V” shape at the hairline.
Pattern characteristics:
- Bilateral temple recession
- Central forelock preservation
- Progressive widening of the “M”
- Eventual connection to crown thinning
- Predictable progression stages
Thinning hair
Existing hair becomes progressively thinner and weaker before complete loss occurs.
Thinning indicators:
- Reduced hair density
- Finer hair texture
- Increased scalp visibility
- Shorter hair length
- Brittle hair quality
Uneven hairline
Irregular patterns of hair loss create an uneven or asymmetrical hairline appearance.
Asymmetry signs:
- Different recession rates on each side
- Patchy hair loss areas
- Irregular hair density
- Jagged hairline borders
- Random thinning spots
Can My Receding Hairline Grow Back?
The potential for hairline regrowth depends on several factors, including the extent of hair loss, treatment timing, and individual response to interventions.
|
Hair Loss Stage |
Regrowth Potential |
Best Treatments |
Timeline |
|
Early thinning |
70-80% |
Medications |
6-12 months |
|
Moderate recession |
40-60% |
Medications + PRP |
12-18 months |
|
Advanced loss |
10-20% |
12-24 months |
|
|
Complete loss |
<5% |
Hair transplant only |
12-24 months |
Factors affecting regrowth:
- Duration of hair loss
- Degree of follicle miniaturization
- Age and overall health
- Treatment compliance
- Genetic factors
Early intervention provides the best opportunity for meaningful regrowth, while advanced cases may require surgical restoration.
Receding hairline in women
Female hairline recession differs significantly from male patterns, typically presenting as diffuse thinning rather than distinct recession lines.
Female characteristics:
- Gradual widening of the part
- Overall hair density reduction
- Preservation of frontal hairline
- Less dramatic recession patterns
- Later onset than men
Common causes in women:
- Hormonal changes (menopause, PCOS)
- Pregnancy and childbirth
- Thyroid disorders
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Stress and lifestyle factors
Treatment considerations:
- Hormone evaluation essential
- Different medication options
- Specialized treatment protocols
- Cosmetic considerations
- Psychological support important
Receding hairline in men
Male hairline recession follows more predictable patterns and typically begins earlier than in women, often starting in the twenties or thirties.
Male characteristics:
- Bilateral temple recession
- M-shaped pattern development
- Progressive crown involvement
- Earlier onset
- More dramatic progression
Age-related progression:
- 20s: 20% show signs
- 30s: 30% affected
- 40s: 40% experience recession
- 50s: 50% have significant loss
- 60s+: 60%+ show advanced patterns
Treatment timing:
- Earlier intervention = better results
- Multiple treatment options available
- Surgical solutions for advanced cases
- Maintenance therapy required
- Realistic expectations important
Does wearing a hat cause a receding hairline?
This common myth has been thoroughly debunked by scientific research. Normal hat wearing does not cause hair loss or receding hairlines.
Facts about hats and hair loss:
- No scientific evidence supporting causation
- Normal hat wearing doesn’t restrict blood flow
- Hair follicles are too deep to be affected
- Genetic factors remain primary cause
- Dirty hats may cause scalp irritation only
When hats might contribute:
- Extremely tight-fitting headwear
- Prolonged wearing of heavy helmets
- Poor hygiene leading to infections
- Mechanical trauma from rough removal
- Pre-existing scalp conditions
Hat wearing benefits:
- Protection from UV damage
- Reduced environmental exposure
- Prevention of hair damage
- Scalp protection
- Style and confidence enhancement
Signs of a Receding Hairline
Recognizing early warning signs enables prompt intervention and better treatment outcomes. Multiple indicators help identify hairline recession progression.
Early warning signs:
- Gradual hairline elevation
- Increased hair shedding during washing
- Thinning at the temples
- Changes in hair texture
- Family history patterns emerging
Progressive indicators:
- Clearly defined recession areas
- M-shaped pattern development
- Increased scalp visibility
- Hair miniaturization
- Asymmetrical patterns
Advanced signs:
- Significant forehead exposure
- Connection to crown thinning
- Minimal remaining hair
- Complete temple baldness
- Established pattern formation
Receding Hairline Stages
Understanding the progression stages helps set realistic treatment expectations and guide therapeutic decisions.
|
Stage |
Description |
Norwood Scale |
Treatment Options |
|
Stage 1 |
Minimal recession |
I-II |
Prevention, medications |
|
Stage 2 |
Temple thinning |
II-III |
Medications, PRP |
|
Stage 3 |
M-shape formation |
III-IV |
Medications, transplant |
|
Stage 4 |
Crown involvement |
IV-V |
Transplant, combination |
|
Stage 5 |
Advanced pattern |
V-VII |
Transplant primary |
Progression timeline:
- Stage 1-2: Often goes unnoticed
- Stage 2-3: Becomes cosmetically apparent
- Stage 3-4: Requires intervention
- Stage 4-5: Surgical options considered
- Stage 5+: Transplant often necessary
Treatment timing considerations:
- Earlier stages: Higher success rates
- Progressive stages: Combination therapy
- Advanced stages: Surgical focus
- Maintenance: Ongoing therapy needed
- Prevention: Ideal for early stages
Receding Hairline Treatment
Modern treatment options offer various approaches to address hairline recession, from pharmaceutical interventions to surgical restoration.
Medications
FDA-approved treatments:
|
Medication |
Mechanism |
Success Rate |
Side Effects |
|
Minoxidil |
Vasodilation |
60-70% |
Minimal |
|
Finasteride |
DHT blocking |
80-90% |
1-2% sexual |
|
Dutasteride |
DHT blocking |
85-95% |
Similar to finasteride |
Application methods:
- Topical solutions and foams
- Oral medications
- Combination therapies
- Compounded formulations
- Sustained-release options
Hair transplant
Surgical restoration provides permanent solutions for advanced hairline recession through follicle redistribution.
Modern techniques:
- FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction)
- FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation)
- DHI (Direct Hair Implantation)
- Robotic assistance
- Advanced closure techniques
Success factors:
- Adequate donor hair supply
- Realistic expectations
- Experienced surgeon selection
- Proper post-operative care
- Long-term maintenance planning
Platelet-rich plasma
PRP therapy utilizes concentrated growth factors to stimulate hair follicle regeneration and improve hair quality.
Treatment protocol:
- Initial series: 3-4 sessions
- Maintenance: Every 6-12 months
- Session duration: 45-60 minutes
- Combination with other treatments
- Minimal downtime required
Red light therapy
Low-level laser therapy stimulates cellular activity and improves hair growth through photobiomodulation.
Treatment specifications:
- Wavelength: 650-670 nm
- Duration: 20-30 minutes per session
- Frequency: 3-4 times weekly
- Home devices available
- FDA-approved options
Style
Strategic hairstyling can effectively camouflage hairline recession while undergoing treatment.
Styling techniques:
- Forward-combed styles
- Textured cuts
- Strategic parting
- Volume-enhancing products
- Professional consultation
Eating healthy diet
Nutritional support plays a crucial role in maintaining hair health and supporting treatment outcomes.
Essential nutrients:
|
Nutrient |
Food Sources |
Daily Requirement |
Hair Benefit |
|
Protein |
Lean meats, eggs |
1g/kg body weight |
Structure building |
|
Iron |
Red meat, spinach |
8-18mg |
Oxygen transport |
|
Biotin |
Nuts, eggs |
30mcg |
Keratin production |
|
Zinc |
Oysters, seeds |
8-11mg |
Follicle function |
PRP therapy
Platelet-Rich Plasma therapy represents an innovative approach using the patient’s own blood components to stimulate hair growth.
Procedure details:
- Blood draw and processing
- Platelet concentration
- Scalp injection
- Growth factor release
- Natural healing enhancement
Hair Transplant
Advanced surgical techniques provide permanent restoration for significant hairline recession.
Planning considerations:
- Donor area assessment
- Hairline design
- Density planning
- Future loss prediction
- Multiple session planning
Lower DHT levels
Reducing dihydrotestosterone levels addresses the primary cause of androgenetic alopecia.
DHT reduction methods:
- 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors
- Natural DHT blockers
- Lifestyle modifications
- Supplement protocols
- Monitoring strategies
Manage stress and anxiety
Stress management plays a crucial role in hair health and treatment success.
Stress reduction techniques:
- Regular exercise
- Meditation and mindfulness
- Adequate sleep
- Professional counseling
- Relaxation techniques
Herbal remedies
Traditional and modern herbal approaches may provide supportive benefits for hair health.
Popular herbal options:
- Saw palmetto
- Pumpkin seed oil
- Green tea extract
- Ginseng
- Rosemary oil
Essential oils
Topical essential oils may provide additional benefits when used as adjunct treatments.
Beneficial oils:
- Rosemary oil
- Peppermint oil
- Lavender oil
- Cedarwood oil
- Thyme oil
What are the stages of a receding hairline?
The Norwood-Hamilton scale provides a standardized classification system for male pattern baldness progression.
Detailed stage breakdown:
|
Stage |
Characteristics |
Percentage Affected |
Age Range |
|
I |
Minimal recession |
5-10% |
18-25 |
|
II |
Temple points |
15-20% |
25-35 |
|
III |
Deep recession |
25-30% |
30-40 |
|
IV |
Crown involvement |
35-40% |
35-45 |
|
V |
Bridge formation |
45-50% |
40-50 |
|
VI |
Crown expansion |
55-60% |
45-55 |
|
VII |
Horseshoe pattern |
65%+ |
50+ |
Progression factors:
- Genetic predisposition strength
- Hormonal sensitivity levels
- Environmental influences
- Lifestyle factors
- Treatment interventions
How to Prevent a Receding Hairline
Prevention strategies focus on modifiable risk factors and early intervention to slow or halt progression.
-
Improve Your Diet
Nutritional optimization supports hair health and may slow hair loss progression.
Dietary recommendations:
- Increase protein intake
- Include omega-3 fatty acids
- Ensure adequate iron levels
- Consume antioxidant-rich foods
- Maintain proper hydration
-
Choose a Shampoo That Promotes Hair Growth
Specialized shampoos can provide scalp health benefits and growth stimulation.
Beneficial ingredients:
- Ketoconazole (anti-DHT)
- Caffeine (stimulation)
- Biotin (strengthening)
- Saw palmetto (DHT blocking)
- Copper peptides (growth)
-
Opt for Another Hair Style
Strategic styling choices can reduce mechanical stress and camouflage early recession.
Protective styles:
- Loose, natural styles
- Minimal tension approaches
- Gentle part lines
- Volume-enhancing techniques
- Professional guidance
-
Scalp Massage
Regular scalp massage improves circulation and may support hair growth.
Massage techniques:
- Gentle circular motions
- 5-10 minutes daily
- Essential oil incorporation
- Professional treatments
- Consistent routine
-
Stress Management
Effective stress management reduces cortisol levels and supports overall hair health.
Management strategies:
- Regular exercise routine
- Meditation practice
- Adequate sleep schedule
- Social support systems
- Professional counseling
-
Finasteride
Early finasteride use can prevent or slow hairline recession progression.
Usage considerations:
- Prescription requirement
- Daily oral administration
- Long-term commitment
- Regular monitoring
- Side effect awareness
-
Minoxidil
Topical minoxidil application can slow recession and stimulate regrowth.
Application protocol:
- Twice daily application
- Direct scalp contact
- Consistent routine
- Long-term use required
- Gradual result appearance
-
PRP therapy
Preventive PRP treatments may help maintain hair density and delay progression.
Preventive protocol:
- Earlier intervention
- Maintenance schedule
- Combination approaches
- Regular assessment
- Realistic expectations
-
Hair transplants
Early transplantation can restore hairline and prevent psychological impacts.
Timing considerations:
- Stable hair loss pattern
- Adequate donor supply
- Realistic expectations
- Long-term planning
- Professional consultation
Home remedies for receding hairline
Natural approaches can complement medical treatments and support overall hair health.
Herbal treatments
Traditional herbs offer potential benefits for hair health and growth stimulation.
Popular herbal options:
- Saw palmetto supplements
- Green tea applications
- Ginseng treatments
- Onion juice applications
- Aloe vera gel
Essential oils
Topical essential oils may provide circulation benefits and growth stimulation.
Application methods:
- Dilution with carrier oils
- Scalp massage incorporation
- Overnight treatments
- Weekly applications
- Patch testing first
Scalp massage
Regular massage improves blood flow and may support hair follicle health.
Technique guidelines:
- Use fingertips, not nails
- Apply gentle pressure
- Circular motions
- 5-10 minute sessions
- Daily consistency
Managing stress
Stress reduction supports overall health and may improve hair growth outcomes.
Stress management tools:
- Deep breathing exercises
- Regular physical activity
- Adequate sleep hygiene
- Social connections
- Professional support
Balanced diet
Nutritional optimization provides building blocks for healthy hair growth.
Key nutritional focus:
- Adequate protein intake
- Essential fatty acids
- Vitamin and mineral balance
- Antioxidant consumption
- Proper hydration
Changing shampoo
Gentle, growth-promoting shampoos can support scalp health and hair retention.
Selection criteria:
- Sulfate-free formulations
- Growth-promoting ingredients
- pH-balanced formulas
- Minimal chemical additives
- Professional recommendations
When to talk with a doctor
Professional consultation helps ensure appropriate treatment selection and monitoring.
Consultation indicators:
- Rapid hair loss progression
- Unusual hair loss patterns
- Associated scalp symptoms
- Family history concerns
- Treatment planning needs
Professional benefits:
- Accurate diagnosis
- Treatment customization
- Progress monitoring
- Side effect management
- Realistic expectation setting
Our experienced intermediary organization at Albania Hair Clinic provides comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment planning for all stages of hairline recession.
FAQ
What is a receding hairline?
A receding hairline is the gradual loss of hair from the front and sides of the scalp, typically starting at the temples and creating an “M” or “V” shaped pattern as it progresses backward.
What causes a receding hairline?
Primary causes include genetics, DHT sensitivity, hormonal changes, aging, stress, poor diet, chemical treatments, and certain medical conditions. Family history is the strongest predictor.
What are the stages of a receding hairline?
The Norwood Hamilton scale classifies seven stages, from minimal temple recession (Stage I) to extensive baldness with only a horseshoe pattern remaining (Stage VII).
Can a receding hairline grow back?
Early stage recession may respond to medications with 70-80% success rates. Advanced cases typically require hair transplantation, while complete hair loss has minimal regrowth potential.
What treatments are available for a receding hairline?
Options include FDA approved medications (minoxidil, finasteride), PRP therapy, low-level laser therapy, hair transplantation, and supportive lifestyle modifications.
How can I prevent a receding hairline?
Prevention involves early medication use, stress management, proper nutrition, gentle hair care, scalp massage, and avoiding damaging styling practices.
Does wearing a hat cause a receding hairline?
No, normal hat wearing does not cause hair loss. This is a myth with no scientific support. Genetics and hormones are the primary causes.
When should I consult a doctor about hair loss?
Seek consultation for rapid progression, unusual patterns, scalp symptoms, or when hair loss impacts quality of life. Early intervention provides better outcomes.